Post-transcriptional RNA regulons affecting cell cycle and proliferation
- PMID: 24882724
- PMCID: PMC4163074
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.05.014
Post-transcriptional RNA regulons affecting cell cycle and proliferation
Abstract
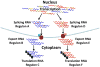
The cellular growth cycle is initiated and maintained by punctual, yet agile, regulatory events involving modifications of cell cycle proteins as well as coordinated gene expression to support cyclic checkpoint decisions. Recent evidence indicates that post-transcriptional partitioning of messenger RNA subsets by RNA-binding proteins help physically localize, temporally coordinate, and efficiently translate cell cycle proteins. This dynamic organization of mRNAs encoding cell cycle components contributes to the overall economy of the cell cycle consistent with the post-transcriptional RNA regulon model of gene expression. This review examines several recent studies demonstrating the coordination of mRNA subsets encoding cell cycle proteins during nuclear export and subsequent coupling to protein synthesis, and discusses evidence for mRNA coordination of p53 targets and the DNA damage response pathway. We consider how these observations may connect to upstream and downstream post-transcriptional coordination and coupling of splicing, export, localization, and translation. Published examples from yeast, nematode, insect, and mammalian systems are discussed, and we consider genetic evidence supporting the conclusion that dysregulation of RNA regulons may promote pathogenic states of growth such as carcinogenesis.
Keywords: Cancer; DNA damage; Posttranscriptional regulation; RNA-binding proteins; Translational control; p53.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
eIF4E is a central node of an RNA regulon that governs cellular proliferation.J Cell Biol. 2006 Nov 6;175(3):415-26. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200607020. Epub 2006 Oct 30. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17074885 Free PMC article.
-
RNA regulons: coordination of post-transcriptional events.Nat Rev Genet. 2007 Jul;8(7):533-43. doi: 10.1038/nrg2111. Nat Rev Genet. 2007. PMID: 17572691 Review.
-
DNA damage activates a spatially distinct late cytoplasmic cell-cycle checkpoint network controlled by MK2-mediated RNA stabilization.Mol Cell. 2010 Oct 8;40(1):34-49. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.018. Mol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20932473 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic analysis of posttranscriptional gene expression.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2010 Mar-Apr;2(2):162-180. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.54. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2010. PMID: 20836020 Review.
-
Biological clocks and the coordination theory of RNA operons and regulons.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007;72:157-65. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2007.72.013. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007. PMID: 18419273 Review.
Cited by
-
Multipurpose RNA maturation factors dysregulate multiple mRNA processing steps simultaneously and provide new therapeutic opportunities.RNA Biol. 2025 Dec;22(1):1-14. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2025.2503040. Epub 2025 Jun 9. RNA Biol. 2025. PMID: 40485569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) mRNA by the RNA-binding proteins human antigen R (HuR) and T-cell intracellular antigen 1 (TIA1).J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 6;290(6):3468-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.631937. Epub 2014 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25519906 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of an RNA-binding protein group on regulating the RSPO-LGR4/5-ZNRF3/RNF43 module and the immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2025 Apr 22;25(1):751. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13874-x. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40264052 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transcriptional regulatory patterns revealed by protein-RNA interactions.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 13;9(1):4302. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40939-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30867517 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria Retrograde Signaling and the UPR mt: Where Are We in Mammals?Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Aug 6;16(8):18224-51. doi: 10.3390/ijms160818224. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26258774 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

