Pilot Study of the Efficacy of 578 nm Copper Bromide Laser Combined with Intralesional Corticosteroid Injection for Treatment of Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars
- PMID: 24882968
- PMCID: PMC4037666
- DOI: 10.5021/ad.2014.26.2.156
Pilot Study of the Efficacy of 578 nm Copper Bromide Laser Combined with Intralesional Corticosteroid Injection for Treatment of Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars
Abstract
Background: Treatments including intralesional corticosteroid injection, pressure therapy, cryotherapy, and various laser therapies have had limited success for keloids and hypertrophic scars.
Objective: This trial evaluated the efficacy of a combination of 578 nm copper bromide laser and the more traditional intralesional corticosteroid injection for the treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars with respect to scar color.
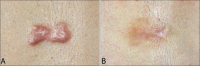
Methods: Keloids or hypertrophic scars of 12 Korean patients were treated five times by the combined treatment at 4-week intervals. Clinical improvement was assessed by the physicians' global assessment (PGA) comparing pre- and post-treatment photographs, as well as 4 weeks after the last treatment. Erythema intensity was quantified using a mexameter.
Results: Most scars showed significant clinical improvement in PGA and decreased erythema intensity after 5 treatments. All patients showed improvements in symptoms like pruritus.
Conclusion: The combined treatment is effective for keloids and hypertrophic scars, especially when the telangiectatic portion of the scars is prominent. The adjunctive use of 578 nm copper bromide laser decreased the telangiectatic side effects of an intralesional corticosteroid injection by reducing the vascular components of scars.
Keywords: 578 nm copper bromide laser; Hypertrophic cicatrix; Intralesional corticosteroid injection; Keloid.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficacy of IPL device combined with intralesional corticosteroid injection for the treatment of keloids and hypertrophic scars with regards to the recovery of skin barrier function: A pilot study.J Dermatolog Treat. 2015 Oct;26(5):481-4. doi: 10.3109/09546634.2015.1024598. Epub 2015 Sep 4. J Dermatolog Treat. 2015. PMID: 25816122
-
Assessment of laser-assisted delivery vs intralesional injection of botulinum toxin A in treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids.Dermatol Ther. 2020 Nov;33(6):e13980. doi: 10.1111/dth.13980. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Dermatol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32638463
-
Treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids using an intralesional 1470 nm bare-fibre diode laser: a novel efficient minimally-invasive technique.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 10;10(1):21694. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78738-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33303965 Free PMC article.
-
Intralesional treatment for keloids and hypertrophic scars: a review.Dermatol Surg. 2013 Dec;39(12):1745-57. doi: 10.1111/dsu.12346. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Dermatol Surg. 2013. PMID: 24299571 Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Corticosteroid in Combination with 5-Fluorouracil in the Treatment of Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Oct;48(19):3765-3778. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04237-1. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 38992250
Cited by
-
Recent developments in the use of intralesional injections keloid treatment.Arch Plast Surg. 2014 Nov;41(6):620-9. doi: 10.5999/aps.2014.41.6.620. Epub 2014 Nov 3. Arch Plast Surg. 2014. PMID: 25396172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
5-Fluorouracil in the Treatment of Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2016 Jun;6(2):169-83. doi: 10.1007/s13555-016-0118-5. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2016. PMID: 27105629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the Effect of Enzymatic Debridement on the Scar Quality in Partial-Thickness Burns to Deep Dermal Burns of the Hand: A Long-Term Evaluation.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Mar 14;60(3):481. doi: 10.3390/medicina60030481. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38541207 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Treatment with Botulinum Toxin and 595-nm Pulsed Dye Laser for Traumatic Scarring.Ann Dermatol. 2015 Dec;27(6):756-8. doi: 10.5021/ad.2015.27.6.756. Epub 2015 Dec 7. Ann Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 26719648 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of laser combination therapy and laser alone therapy for keloid: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lasers Med Sci. 2022 Mar;37(2):1127-1138. doi: 10.1007/s10103-021-03364-4. Epub 2021 Jul 20. Lasers Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 34283306
References
-
- English RS, Shenefelt PD. Keloids and hypertrophic scars. Dermatol Surg. 1999;25:631–638. - PubMed
-
- Khatri KA, Mahoney DL, McCartney MJ. Laser scar revision: A review. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2011;13:54–62. - PubMed
-
- Wolfram D, Tzankov A, Pülzl P, Piza-Katzer H. Hypertrophic scars and keloids--a review of their pathophysiology, risk factors, and therapeutic management. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35:171–181. - PubMed
-
- Connell PG, Harland CC. Treatment of keloid scars with pulsed dye laser and intralesional steroid. J Cutan Laser Ther. 2000;2:147–150. - PubMed
-
- Alster TS, West TB. Treatment of scars: a review. Ann Plast Surg. 1997;39:418–432. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

