Assessment of vascular endothelial growth factor in formalin fixed, paraffin embedded colon cancer specimens by means of a well-based reverse phase protein array
- PMID: 24883046
- PMCID: PMC4039052
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-5956-12-27
Assessment of vascular endothelial growth factor in formalin fixed, paraffin embedded colon cancer specimens by means of a well-based reverse phase protein array
Abstract
Background: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a critical pro-angiogenic factor, found in a number of cancers, and a target of therapy. It is typically assessed by immunohistochemistry (IHC) in clinical research. However, IHC is not a quantitative assay and is rarely reproducible. We compared VEGF levels in colon cancer by IHC and a quantitative immunoassay on proteins isolated from formalin fixed, paraffin embedded tissues.
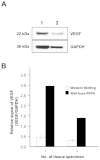
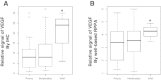
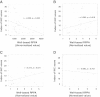
Results: VEGF expression was studied by means of a well-based reverse phase protein array (RPPA) and immunohistochemistry in 69 colon cancer cases, and compared with various clinicopathologic factors. Protein lysates derived from formalin fixed, paraffin embedded tissue contained measurable immunoreactive VEGF molecules. The VEGF expression level of well differentiated colon cancer was significantly higher than those with moderately and poorly differentiated carcinomas by immunohistochemistry (P = 0.04) and well-based RPPA (P = 0.04). VEGF quantification by well-based RPPA also demonstrated an association with nodal metastasis status (P = 0.05). In addition, the normalized VEGF value by well-based RPPA correlated (r = 0.283, P = 0.018). Furthermore, subgroup analysis by histologic type revealed that adenocarcinoma cases showed significant correlation (r = 0.315, P = 0.031) between well-based RPPA and IHC.
Conclusions: The well-based RPPA method is a high throughput and sensitive approach, is an excellent tool for quantification of marker proteins. Notably, this method may be helpful for more objective evaluation of protein expression in cancer patients.
Keywords: Colon cancer; Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded; Immunohistochemistry; Reverse-phase protein array; Vascular endothelial growth factor.
Figures

Similar articles
-
HER-2 assessment in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded breast cancer tissue by well-based reverse phase protein array.Clin Proteomics. 2014 Oct 1;11(1):36. doi: 10.1186/1559-0275-11-36. eCollection 2014. Clin Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 25838812 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical utility of reverse phase protein array for molecular classification of breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Jan;155(1):25-35. doi: 10.1007/s10549-015-3654-2. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 26661092
-
Multiple protein analysis of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissue samples with reverse phase protein arrays.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013 Sep;12(9):2615-22. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M112.023051. Epub 2013 May 7. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23653450 Free PMC article.
-
Intracranial meningiomas, the VEGF-A pathway, and peritumoral brain oedema.Dan Med J. 2013 Apr;60(4):B4626. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 23651727 Review.
-
Reverse Phase Protein Arrays-Quantitative Assessment of Multiple Biomarkers in Biopsies for Clinical Use.Microarrays (Basel). 2015 Mar 24;4(2):98-114. doi: 10.3390/microarrays4020098. Microarrays (Basel). 2015. PMID: 27600215 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of a panel of tumor markers for the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant effusions by well-based reverse phase protein array.Diagn Pathol. 2015 May 29;10:53. doi: 10.1186/s13000-015-0290-4. Diagn Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26022333 Free PMC article.
-
HER-2 assessment in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded breast cancer tissue by well-based reverse phase protein array.Clin Proteomics. 2014 Oct 1;11(1):36. doi: 10.1186/1559-0275-11-36. eCollection 2014. Clin Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 25838812 Free PMC article.
-
Gel formulations of Merremia mammosa (Lour.) accelerated wound healing of the wound in diabetic rats.J Tradit Complement Med. 2019 Dec 9;11(1):38-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2019.12.002. eCollection 2021 Jan. J Tradit Complement Med. 2019. PMID: 33511060 Free PMC article.
-
Role of VEGF, CD105, and CD31 in the Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer Cases.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2019 Mar;50(1):23-34. doi: 10.1007/s12029-017-0014-y. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2019. PMID: 29110224
-
A melanin-bleaching methodology for molecular and histopathological analysis of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue.Lab Invest. 2016 Oct;96(10):1116-27. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2016.90. Epub 2016 Aug 22. Lab Invest. 2016. PMID: 27548802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zebrowski BK, Yano S, Liu W, Shaheen RM, Hicklin DJ, Putnam JB Jr, Ellis LM. Vascular endothelial growth factor levels and induction of permeability in malignant pleural effusions. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:3364–3368. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi Y, Kitadai Y, Bucana CD, Cleary KR, Ellis LM. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor, KDR, correlates with vascularity, metastasis, and proliferation of human colon cancer. Cancer Res. 1995;55:3964–3968. - PubMed
-
- Perrone G, Vincenzi B, Santini D, Verzi A, Tonini G, Vetrani A, Rabitti C. Correlation of p53 and bcl-2 expression with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), microvessel density (MVD) and clinico-pathological features in colon cancer. Cancer Lett. 2004;208:227–234. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2003.11.032. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

