MDCT of Small Bowel Obstruction: How Reliable Are Oblique Reformatted Images in Localizing Point of Transition?
- PMID: 24883057
- PMCID: PMC4026987
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/815802
MDCT of Small Bowel Obstruction: How Reliable Are Oblique Reformatted Images in Localizing Point of Transition?
Abstract
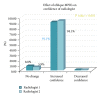
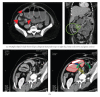
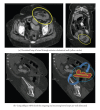
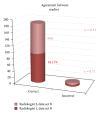
The goal of this study is to prospectively assess the additional value of oblique reformatted images for localizing POT, having surgery as a reference standard. Materials and Methods. 102 consecutive patients with suspected small bowel obstruction (SBO) underwent 64-slice multidetector row CT (MDCT) using surgical findings as reference standard. Two independent GI radiologists reviewed the CT scans to localize the exact POT by evaluating axial images (data set A) followed by axial, coronal, and oblique MPR images. CT findings were compared to surgical findings in terms of diagnostic performance. McNemar's test was used to detect any statistical difference in POT evaluation between datasets A and B. Kappa statistics were applied for measuring agreement between two readers. Results. There was a diagnostic improvement of 9.9% in the case of the less experienced radiologist in localizing POT by using oblique reformatted images. The more experienced radiologist showed diagnostic improvement by 12.9%.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of Transition Zone in Bowel Obstruction via Curved Multiplanar Reformations with Multidetector Computed Tomography.Cureus. 2019 Mar 11;11(3):e4233. doi: 10.7759/cureus.4233. Cureus. 2019. PMID: 31123655 Free PMC article.
-
Four-section multidetector computed tomographic imaging of bowel obstruction: usefulness of axial and coronal plane combined reading.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2007 Jul-Aug;31(4):499-507. doi: 10.1097/01.rct.0000238013.87802.3c. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2007. PMID: 17882022
-
Urothelial-phase thin-section MDCT of the bladder in patients with hematuria: added value of multiplanar reformatted images.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021 May;46(5):2025-2031. doi: 10.1007/s00261-020-02819-6. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021. PMID: 33079253
-
Multidetector row computed tomography of small bowel obstruction.Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2008 Oct;29(5):308-21. doi: 10.1053/j.sult.2008.06.004. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2008. PMID: 18853838 Review.
-
Bowel obstruction: comparison between multidetector-row CT axial and coronal planes.Abdom Imaging. 2007 May-Jun;32(3):310-6. doi: 10.1007/s00261-006-9065-4. Epub 2006 Aug 26. Abdom Imaging. 2007. PMID: 16937232 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Multidetector Computed Tomography with Multiplanar and Curved Multiplanar Reformations in the Detection of Cause of Intestinal Obstruction: A Tertiary Care Experience.Cureus. 2020 Mar 29;12(3):e7464. doi: 10.7759/cureus.7464. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 32351843 Free PMC article.
-
Computed Tomography Image Segmentation of the Proximal Colon by U-Net for the Clinical Study of Somatostatin Combined with Intestinal Obstruction Catheter.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Jan 18;2022:6868483. doi: 10.1155/2022/6868483. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. PMID: 35087602 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic utility of CT for small bowel obstruction: Systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 30;14(12):e0226740. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226740. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31887146 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Multi-Detector Computed Tomography in the Diagnosis of Intestinal Obstruction.Cureus. 2023 Jan 13;15(1):e33730. doi: 10.7759/cureus.33730. eCollection 2023 Jan. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36788830 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical impact of computed tomography in the emergency department in nontraumatic chest and abdominal conditions.Emerg Radiol. 2018 Aug;25(4):393-398. doi: 10.1007/s10140-018-1592-0. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Emerg Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29536277
References
-
- Foster NM, McGory ML, Zingmond DS, Ko CY. Small bowel obstruction: a population-based appraisal. Journal of the American College of Surgeons. 2006;203(2):170–176. - PubMed
-
- Rosen MP, Siewert B, Sands DZ, Bromberg R, Edlow J, Raptopoulos V. Value of abdominal CT in the emergency department for patients with abdominal pain. European Radiology. 2003;13(2):418–424. - PubMed
-
- Frager D, Medwid SW, Baer JW, Mollinelli B, Friedman M. CT of small-bowel obstruction: value in establishing the diagnosis and determining the degree and cause. American Journal of Roentgenology. 1994;162(1):37–41. - PubMed
-
- Silen W, Hein MF, Goldman L. Strangulation obstruction of the small intestine. Archives of Surgery. 1962;85:121–129. - PubMed
-
- Lappas JC, Reyes BL, Maglinte DDT. Abdominal radiography findings in small-bowel obstruction: relevance to triage for additional diagnostic imaging. American Journal of Roentgenology. 2001;176(1):167–174. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

