Evaluation of the Antihyperuricemic Activity of Phytochemicals from Davallia formosana by Enzyme Assay and Hyperuricemic Mice Model
- PMID: 24883071
- PMCID: PMC4026843
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/873607
Evaluation of the Antihyperuricemic Activity of Phytochemicals from Davallia formosana by Enzyme Assay and Hyperuricemic Mice Model
Abstract
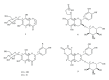
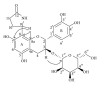
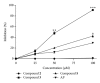
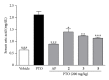
Abnormal serum urate levels are recognized as a critical factor in the progression of several chronic diseases. To evaluate the antihyperuricemic effect of Davallia formosana, the inhibitory activities of 15 isolated phytochemicals, including five novel compounds of 6,8-dihydroxychromone-7-C- β -d-glucopyranoside (1), 6,8,3',4'-tetrahydroxyflavanone-7-C- β -d-glucopyranoside (2), 6,8,4'-trihydroxyflavanone-7-C- β -d-glucopyranoside (3), 8-(2-pyrrolidinone-5-yl)-catechin-3-O- β -d-allopyranoside (4), and epiphyllocoumarin-3-O- β -d-allopyranoside (5), were examined against xanthine oxidase (XOD) and in a potassium oxonate-(PTO-) induced acute hyperuricemic mice model. The results indicated that compounds 3 and 5 significantly inhibited XOD activity in vitro and reduced serum uric acid levels in vivo. This is the first report providing new insights into the antihyperuricemic activities of flavonoid glycosides which can possibly be developed into potential hypouricemic agents.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Flavonoids and phenylethanoid glycosides from Lippia nodiflora as promising antihyperuricemic agents and elucidation of their mechanism of action.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 24;176:485-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.11.025. Epub 2015 Nov 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26593216
-
The Hypouricemic Effect of Balanophora laxiflora Extracts and Derived Phytochemicals in Hyperuricemic Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:910152. doi: 10.1155/2012/910152. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012. PMID: 22778779 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemicals from Acacia confusa heartwood extracts reduce serum uric acid levels in oxonate-induced mice: their potential use as xanthine oxidase inhibitors.J Agric Food Chem. 2010 Sep 22;58(18):9936-41. doi: 10.1021/jf102689k. J Agric Food Chem. 2010. PMID: 20806936
-
Effects of cassia oil on serum and hepatic uric acid levels in oxonate-induced mice and xanthine dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase activities in mouse liver.J Ethnopharmacol. 2006 Feb 20;103(3):357-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2005.08.040. Epub 2005 Sep 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16182482
-
Effects of ChondroT on potassium Oxonate-induced Hyperuricemic mice: downregulation of xanthine oxidase and urate transporter 1.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Jan 8;19(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2415-2. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 30621705 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Phytochemicals from fern species: potential for medicine applications.Phytochem Rev. 2017;16(3):379-440. doi: 10.1007/s11101-016-9488-7. Epub 2017 Jan 28. Phytochem Rev. 2017. PMID: 32214919 Free PMC article.
-
Uricase alkaline enzymosomes with enhanced stabilities and anti-hyperuricemia effects induced by favorable microenvironmental changes.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 29;7:20136. doi: 10.1038/srep20136. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26823332 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Muntingia calabura L. Stem Bark Extracts on Uric Acid Concentration and Renal Histopathology in Diabetic Rats.Medicina (Kaunas). 2019 Oct 16;55(10):695. doi: 10.3390/medicina55100695. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019. PMID: 31623288 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy and Mechanism of Chinese Herbal Medicines in Lowering Serum Uric Acid Levels: A Systematic Review.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 25;11:578318. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.578318. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33568990 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becker MA, Jolly M. Hyperuricemia and associated diseases. Rheumatic Disease Clinics of North America. 2006;32(2):275–293. - PubMed
-
- Wortmann RL. Gout and hyperuricemia. Current Opinion in Rheumatology. 2002;14(3):281–286. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal A, Banerjee A, Banerjee UC. Xanthine oxidoreductase: a journey from purine metabolism to cardiovascular excitation-contraction coupling. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology. 2011;31(3):264–280. - PubMed
-
- Harrison R. Structure and function of xanthine oxidoreductase: where are we now? Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2002;33(6):774–797. - PubMed
-
- Elion GB. The purine path to chemotherapy. Science. 1989;244(4900):41–47. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

