An Immunomodulatory Protein (Ling Zhi-8) from a Ganoderma lucidum Induced Acceleration of Wound Healing in Rat Liver Tissues after Monopolar Electrosurgery
- PMID: 24883073
- PMCID: PMC4026841
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/916531
An Immunomodulatory Protein (Ling Zhi-8) from a Ganoderma lucidum Induced Acceleration of Wound Healing in Rat Liver Tissues after Monopolar Electrosurgery
Abstract
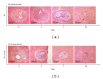
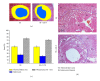
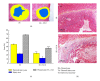
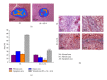
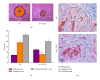
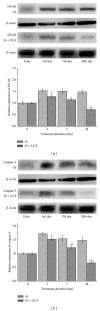
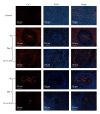
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of an immunomodulatory protein (Ling Zhi-8, LZ-8) on wound healing in rat liver tissues after monopolar electrosurgery. Animals were sacrificed for evaluations at 0, 3, 7, and 28 days postoperatively. It was found that the wound with the LZ-8 treatment significantly increases wound healing. Western blot analysis clearly indicated that the expression of NF-κB was decreased at 3, 7, and 28 days when liver tissues were treated with LZ-8. Moreover, caspase-3 activity of the liver tissue also significantly decreases at 7 and 28 days, respectively. DAPI staining and TUNEL assays revealed that only a minimal dispersion of NF-κB was found on the liver tissue treated with LZ-8 at day 7 as compared with day 3 and tissues without LZ-8 treatment. Similarly, apoptosis was decreased on liver tissues treated with LZ-8 at 7 days when compared to the control (monopolar electrosurgery) tissues. Therefore, the analytical results demonstrated that LZ-8 induced acceleration of wound healing in rat liver tissues after monopolar electrosurgery.
Figures

References
-
- Liboon J, Funkhouser W, Terris DJ. A comparison of mucosal incisions made by scalpel, CO2 laser, electrocautery, and constant-voltage electrocautery. Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery. 1997;116(3):379–385. - PubMed
-
- Carew JF, Ward RF, LaBruna A, Torzilli PA, Schley WS. Effects of scalpel, electrocautery, and CO2 and KTP lasers on wound healing in rat tongues. The Laryngoscope. 1998;108(3):373–380. - PubMed
-
- Pearce JA. Electrosurgery. New York, NY, USA: John Wiley & Sons; 1986.
-
- Maness WL, Rober FW, Clark RE, Cataldo E, Haddad AW. Tissue damage from electrosurgical power output variations in hamster tongues. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry. 1979;42(4):456–460. - PubMed
-
- Maness WL, Roeber FW, Clark RE, Cataldo E, Riis D, Haddad AW. Histologic evaluation of electrosurgery with varying frequency and waveform. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry. 1978;40(3):304–308. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

