Diagnosis and management of intestinal Behçet's disease
- PMID: 24883128
- PMCID: PMC4037558
- DOI: 10.1007/s12328-014-0488-0
Diagnosis and management of intestinal Behçet's disease
Abstract
Behçet's disease (BD) is a chronic relapsing disease with multiple organ system involvement characterized clinically by oral and genital aphthae, cutaneous lesions, and ophthalmological, neurological, and/or gastrointestinal manifestations. Little clinical evidence is available regarding the management of patients with intestinal BD, despite recognition that the presence of intestinal lesions is a poor prognostic factor, causing perforation and massive bleeding. Many recent case reports have suggested that anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF)α monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are effective in patients with intestinal BD. Adalimumab, a fully human anti-TNFα mAb, has been approved in Japan for the treatment of intestinal BD. Here, we review the pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of intestinal BD, including evidence of the efficacy of anti-TNFα mAbs.
Keywords: Adalimumab; Anti-TNFα mAb; Intestinal Behçet’s disease; Trisomy 8.
Figures
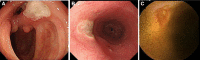

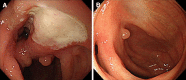
References
-
- Behçet H. Uber rezidivierende, aphthose, durch ein Virus verursachte Geschwire am Mund, am Auge und an den Genitalen. Dermatol Wochenschr. 1937;105:1152–1157.
-
- Garton RA, Ghate JV, Jorizzo JL. Behçet’s disease. In: Harris ED Jr, Budd RC, Genovese MC, Firestein GS, Sargent JS, Sledge CB, editors. Textbook of rheumatology. 7. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2005.
-
- Criteria for diagnosis of Behçet’s disease International study group for Behçet’s disease. Lancet. 1990;335:1078–1080. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

