Quantitative Analysis of Panax ginseng by FT-NIR Spectroscopy
- PMID: 24883224
- PMCID: PMC4026986
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/741571
Quantitative Analysis of Panax ginseng by FT-NIR Spectroscopy
Abstract
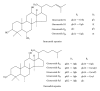
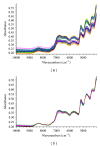
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS), a rapid and efficient tool, was used to determine the total amount of nine ginsenosides in Panax ginseng. In the study, the regression models were established using multivariate regression methods with the results from conventional chemical analytical methods as reference values. The multivariate regression methods, partial least squares regression (PLSR) and principal component regression (PCR), were discussed and the PLSR was more suitable. Multiplicative scatter correction (MSC), second derivative, and Savitzky-Golay smoothing were utilized together for the spectral preprocessing. When evaluating the final model, factors such as correlation coefficient (R (2)) and the root mean square error of prediction (RMSEP) were considered. The final optimal results of PLSR model showed that root mean square error of prediction (RMSEP) and correlation coefficients (R (2)) in the calibration set were 0.159 and 0.963, respectively. The results demonstrated that the NIRS as a new method can be applied to the quality control of Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Determination of Ginsenosides Amount and Geographical Origins of Ginseng by NIR Spectroscopy].Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 2015 Jul;35(7):1885-8. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 2015. PMID: 26717745 Chinese.
-
[Study on the Rapid Evaluation of Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen (TVB-N) of Mutton by Hyperspectral Imaging Technique].Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 2016 Mar;36(3):806-10. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 2016. PMID: 27400528 Chinese.
-
Rapid Detection of Volatile Oil in Mentha haplocalyx by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Chemometrics.Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Jul-Sep;13(51):439-445. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.211026. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017. PMID: 28839369 Free PMC article.
-
Dissolution testing of isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide and ethambutol tablets using near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) and multivariate calibration.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012 Jan 5;57:115-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2011.08.029. Epub 2011 Aug 24. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012. PMID: 21908131
-
Quantitative Analysis of Salidroside and p-Tyrosol in the Traditional Tibetan Medicine Rhodiola crenulata by Fourier Transform Near-Infrared Spectroscopy.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2016;64(4):289-96. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c15-00558. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2016. PMID: 27039830
Cited by
-
Remarkable impact of steam temperature on ginsenosides transformation from fresh ginseng to red ginseng.J Ginseng Res. 2018 Jul;42(3):277-287. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2017.02.003. Epub 2017 Feb 27. J Ginseng Res. 2018. PMID: 29983609 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of propranolol hydrochloride in pharmaceutical preparations using near infrared spectrometry with fiber optic probe and multivariate calibration methods.J Anal Methods Chem. 2015;2015:795102. doi: 10.1155/2015/795102. Epub 2015 Mar 12. J Anal Methods Chem. 2015. PMID: 25861516 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid discrimination of Panax ginseng powder adulterated with various root plants by FT-IR spectroscopy coupled with multivariate analysis.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2023 Nov 17;33(4):805-815. doi: 10.1007/s10068-023-01423-w. eCollection 2024 Mar. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38371692 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Study on Analysis of Ginsenosides in American Ginseng Root Residue by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS and UPLC-HRMS-MS/MS.Molecules. 2022 May 11;27(10):3071. doi: 10.3390/molecules27103071. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35630548 Free PMC article.
-
Multivariate Calibration and Model Integrity for Wood Chemistry Using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy.J Anal Methods Chem. 2015;2015:429846. doi: 10.1155/2015/429846. Epub 2015 Oct 20. J Anal Methods Chem. 2015. PMID: 26576321 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chinese Pharmacopeia Committee. Pharmacopeia of People’s Republic of China. Beijing, China: Chinese Medicine Science and Technology; 2010.
-
- Shibata S, Fujita M, Itokawa H, Tanako O, Ishii T. Studies on the constituents of Japanese and Chinese crude drugs. XI. Panaxadiol, a sapogenin of ginseng roots. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 1963;11(6):759–761. - PubMed
-
- Popovich DG, Yeo C-R, Zhang W. Ginsenosides derived from Asian (Panax ginseng), American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius) and potential cytoactivityl. International Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2012;6(1):56–62.
-
- Wei Y, Zhao W, Zhang Q, Zhao Y, Zhang Y. Purification and characterization of a novel and unique ginsenoside Rg1-hydrolyzing β-d-Glucosidase from Penicillium sclerotiorum . Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica. 2011;43(3):226–231. - PubMed
-
- Christensen LP. Chapter 1 Ginsenosides: chemistry, biosynthesis, analysis, and potential health effects. Advances in Food and Nutrition Research. 2008;55:1–99. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

