Retrospective cohort study of anti-tumor necrosis factor agent use in a veteran population
- PMID: 24883246
- PMCID: PMC4034612
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.385
Retrospective cohort study of anti-tumor necrosis factor agent use in a veteran population
Abstract
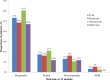
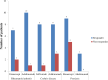
Introduction. Anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) agents are effective for several immunologic conditions (rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Crohn's disease (CD), and psoriasis). The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of anti-TNF agents via chart review. Methods. Single-site, retrospective cohort study that evaluated the efficacy and safety of anti-TNF agents in veterans initiated between 2010 and 2011. Primary aim evaluated response at 12 months post-index date. Secondary aims evaluated initial response prior to 12 months post-index date and infection events. Results. A majority of patients were prescribed anti-TNF agents for CD (27%) and RA (24%). Patients were initiated on etanercept (41%), adalimumab (40%), and infliximab (18%) between 2010 and 2011. No differences in patient demographics were reported. Response rates were high overall. Sixty-five percent of etanercept patients, 82% of adalimumab patients, and 59% of infliximab patients were either partial or full responders, respectively. Approximately 16%, 11%, and 12% of etanercept, adalimumab, and infliximab were non-responders, respectively. Infections between the groups were non-significant. Etanercept and adalimumab patients had higher but non-significant odds of being a responder relative to infliximab. Conclusions. Most patients initiated with anti-TNF agent were responders at 12 months follow-up for all indications in a veteran population.
Keywords: Adalimumab; Certolizumab; Cohort study; Crohn’s disease; Etanercept; Formulary management; Infliximab; Rheumatoid arthritis; Tumor necrosis factor; Veterans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Agents in Biologic-Naive Patients With Crohn's Disease.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Aug;14(8):1120-1129.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2016.03.038. Epub 2016 Apr 4. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 27058635 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment persistence with adalimumab, etanercept, or infliximab in combination with methotrexate and the effects on health care costs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Ther. 2008 Jul;30(7):1375-84. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(08)80063-x. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 18691998
-
Adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab utilization patterns and drug costs among rheumatoid arthritis patients.J Med Econ. 2012;15(2):332-9. doi: 10.3111/13696998.2011.649325. Epub 2012 Jan 6. J Med Econ. 2012. PMID: 22168788
-
Serious infection during etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: A literature review.Int J Rheum Dis. 2016 Jun;19(6):536-50. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12659. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016. PMID: 26200188 Review.
-
A PEGylated Fab' fragment against tumor necrosis factor for the treatment of Crohn disease: exploring a new mechanism of action.BioDrugs. 2008;22(5):331-7. doi: 10.2165/00063030-200822050-00005. BioDrugs. 2008. PMID: 18778114 Review.
References
-
- Agarwal SK. Core management principles in rheumatoid arthritis to help guide managed care professionals. Journal of Managed Care Pharmacy. 2011a;17:S03–S08. - PubMed
-
- Ancuţa C, Ancuţa E, Miu S, Iordache C, Belibou C, Chirieac R. Adalimumab therapy in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Revista medico-chirurgicala a Societatii de Medici si Naturalisti din Iasi. 2009;113:710–715. - PubMed
-
- Bathon JM, Martin RW, Fleischmann RM, Tesser JR, Schiff MH, Keystone EC, Genovese MC, Wasko MC, Moreland LW, Weaver AL, Markenson J, Finck BK. A comparison of etanercept and methotrexate in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. New England Journal of Medicine. 2000;343:1586–1593. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200011303432201. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources