DoMINO: Donor milk for improved neurodevelopmental outcomes
- PMID: 24884424
- PMCID: PMC4032387
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2431-14-123
DoMINO: Donor milk for improved neurodevelopmental outcomes
Abstract
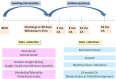
Background: Provision of mother's own milk is the optimal way to feed infants, including very low birth weight infants (VLBW, <1500 g). Importantly for VLBW infants, who are at elevated risk of neurologic sequelae, mother's own milk has been shown to enhance neurocognitive development. Unfortunately, the majority of mothers of VLBW infants are unable to provide an adequate supply of milk and thus supplementation with formula or donor milk is necessary. Given the association between mother's own milk and neurodevelopment, it is important to ascertain whether provision of human donor milk as a supplement may yield superior neurodevelopmental outcomes compared to formula.Our primary hypothesis is that VLBW infants fed pasteurized donor milk compared to preterm formula as a supplement to mother's own milk for 90 days or until hospital discharge, whichever comes first, will have an improved cognitive outcome as measured at 18 months corrected age on the Bayley Scales of Infant Development, 3(rd) ed. Secondary hypotheses are that the use of pasteurized donor milk will: (1) reduce a composite of death and serious morbidity; (2) support growth; and (3) improve language and motor development. Exploratory research questions include: Will use of pasteurized donor milk: (1) influence feeding tolerance and nutrient intake (2) have an acceptable cost effectiveness from a comprehensive societal perspective?
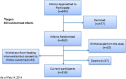
Methods/design: DoMINO is a multi-centre, intent-to-treat, double blinded, randomized control trial. VLBW infants (n = 363) were randomized within four days of birth to either (1) pasteurized donor milk or (2) preterm formula whenever mother's own milk was unavailable. Study recruitment began in October 2010 and was completed in December 2012. The 90 day feeding intervention is complete and long-term follow-up is underway.
Discussion: Preterm birth and its complications are a leading cause long-term morbidity among Canadian children. Strategies to mitigate this risk are urgently required. As mother's own milk has been shown to improve neurodevelopment, it is essential to ascertain whether pasteurized donor milk will confer the same advantage over formula without undue risks and at acceptable costs. Knowledge translation from this trial will be pivotal in setting donor milk policy in Canada and beyond.
Trial registration: ISRCTN35317141; Registered 10 August 2010.
Figures
References
-
- Qiu X, Lee SK, Tan K, Piedboeuf B, Canning R. Comparison of singleton and multiple-birth outcomes of infants born at or before 32 weeks of gestation. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;111(2 Pt 1):365–371. - PubMed
-
- Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Bell EF, Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Walsh MC, Hale EC, Newman NS, Schibler K, Carlo WA, Kennedy KA, Poindexter BB, Finer NN, Ehrenkranz RA, Duara S, Sanchez PJ, O’Shea TM, Goldberg RN, Van Meurs KP, Faix RG, Phelps DL, Frantz ID 3rd, Watterberg KL, Saha S, Das A, Higgins RD. Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. Neonatal outcomes of extremely preterm infants from the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics. 2010;126:443–456. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saigal S, Doyle LW. An overview of mortality and sequelae of preterm birth from infancy to adulthood. Lancet. 2008;371:261–269. - PubMed
-
- Ehrenkranz RA, Dusick AM, Vohr BR, Wright LL, Wrage LA, Poole WK. Growth in the neonatal intensive care unit influences neurodevelopmental and growth outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 2006;117:1253–1261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous