Personality dimensions of schizophrenia patients compared to control subjects by gender and the relationship with illness severity
- PMID: 24884428
- PMCID: PMC4039307
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-244X-14-151
Personality dimensions of schizophrenia patients compared to control subjects by gender and the relationship with illness severity
Abstract
Background: Personality traits and schizophrenia present gender differences; however, gender has not been considered in most studies on personality and schizophrenia. This study aims to identify the different personality dimensions of schizophrenia patients and healthy control subjects by gender and to explore the relationship between personality dimensions and illness severity variables by analyzing data for males and females separately.
Methods: Temperament and Character Inventory-Revised dimensions were compared by gender between 161 schizophrenia patients and 214 healthy controls from a population-based sample using independent t-tests. We then investigated whether personality dimensions are related to illness severity variables using correlation analyses and bivariate logistic regression, also by gender.
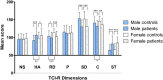
Results: The patients had significantly higher scores for harm avoidance (HA) and self-transcendence (ST) and lower scores for reward dependence (RD), cooperativeness (C), and self-directedness (SD) than the controls. Similar results were obtained when the sample was stratified by gender, however the differences were higher and more significant for HA among males and for RD among females. The number of admissions to a psychiatric hospital positively correlated with novelty seeking (NS) in males and negatively with SD in females. In males, SD and ST negatively correlated with the number of suicide attempts.
Conclusions: Male and female patients present difficulties for regulating and adapting behavior to achieve goals (SD) and for identifying and accepting others (C), as well as a great sense of spirituality and universe identification (ST). However, male patients are more characterized by being fearful, doubtful and easily fatigued (HA), while female patients are characterized by presenting difficulties maintaining and pursuing associated reward behaviors (RD). Furthermore, male and female patients who are frequently admitted to psychiatric hospitals and male patients who attempt suicide should be evaluated regarding their personality dimensions. Future studies assessing the relationship between personality dimensions and the clinical features of schizophrenia should consider gender differences.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Personality factors in depressive disorders: contribution of the psychobiologic model developed by Cloninger].Encephale. 2002 Jul-Aug;28(4):363-73. Encephale. 2002. PMID: 12232546 Review. French.
-
Personality in schizophrenia assessed with the Temperament and Character Inventory (TCI).Psychiatry Res. 2008 Aug 15;160(2):175-83. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2007.05.015. Epub 2008 Jul 7. Psychiatry Res. 2008. PMID: 18602163
-
Personality traits and schizophrenia: evidence from a case-control study and meta-analysis.Psychiatry Res. 2012 Jun 30;198(1):7-11. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2011.12.018. Epub 2012 Mar 5. Psychiatry Res. 2012. PMID: 22397918
-
The Risk Model of Developing Schizophrenia Based on Temperament and Character.Psychiatr Danub. 2018 Mar;30(1):57-63. doi: 10.24869/psyd.2018.57. Psychiatr Danub. 2018. PMID: 29546859
-
Differences in temperament and character inventory (TCI) profile between suicidal and nonsuicidal psychiatric outpatients.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Sep 2;101(35):e30202. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030202. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36107514 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Integrating trauma, self-disturbances, cognitive biases, and personality into a model for the risk of psychosis: a longitudinal study in a non-clinical sample.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2022 Sep;272(6):1073-1085. doi: 10.1007/s00406-021-01355-8. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 34859297 Free PMC article.
-
Family caregivers and outcome of people with schizophrenia in rural China: 14-year follow-up study.Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2016 Apr;51(4):513-20. doi: 10.1007/s00127-015-1169-0. Epub 2016 Jan 2. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2016. PMID: 26724945
-
The value of novelty in schizophrenia.Schizophr Res. 2018 Feb;192:287-293. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2017.05.007. Epub 2017 May 9. Schizophr Res. 2018. PMID: 28495493 Free PMC article.
-
Disability and premorbid adjustment in schizophrenia: A retrospective analysis.S Afr J Psychiatr. 2022 Dec 19;28:1853. doi: 10.4102/sajpsychiatry.v28i0.1853. eCollection 2022. S Afr J Psychiatr. 2022. PMID: 36569810 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of parvalbumin-expressing interneurons results in complex behavioral changes.Mol Psychiatry. 2015 Dec;20(12):1499-507. doi: 10.1038/mp.2014.192. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Mol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25623945 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

