The effect of rituximab therapy on immunoglobulin levels in patients with multisystem autoimmune disease
- PMID: 24884562
- PMCID: PMC4038057
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-15-178
The effect of rituximab therapy on immunoglobulin levels in patients with multisystem autoimmune disease
Abstract
Background: Rituximab is a B cell depleting anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody. CD20 is not expressed on mature plasma cells and accordingly rituximab does not have immediate effects on immunoglobulin levels. However, after rituximab some patients develop hypogammaglobulinaemia.
Methods: We performed a single centre retrospective review of 177 patients with multisystem autoimmune disease receiving rituximab between 2002 and 2010. The incidence, severity and complications of hypogammaglobulinaemia were investigated.
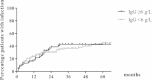
Results: Median rituximab dose was 6 g (1-20.2) and total follow-up was 8012 patient-months. At first rituximab, the proportion of patients with IgG <6 g/L was 13% and remained stable at 17% at 24 months and 14% at 60 months. Following rituximab, 61/177 patients (34%) had IgG <6 g/L for at least three consecutive months, of whom 7/177 (4%) had IgG <3 g/L. Low immunoglobulin levels were associated with higher glucocorticoid doses during follow up and there was a trend for median IgG levels to fall after ≥ 6 g rituximab. 45/115 (39%) with IgG ≥ 6 g/L versus 26/62 (42%) with IgG <6 g/L experienced severe infections (p=0.750). 6/177 patients (3%) received intravenous immunoglobulin replacement therapy, all with IgG <5 g/L and recurrent infection.
Conclusions: In multi-system autoimmune disease, prior cyclophosphamide exposure and glucocorticoid therapy but not cumulative rituximab dose was associated with an increased incidence of hypogammaglobulinaemia. Severe infections were common but were not associated with immunoglobulin levels. Repeat dose rituximab therapy appears safe with judicious monitoring.
Figures

References
-
- Jones RB, Tervaert JW, Hauser T, Luqmani R, Morgan MD, Peh CA, Savage CO, Segelmark M, Tesar V, van Paassen P, Walsh D, Walsh M, Westman K, Jayne DR. European Vasculitis Study Group. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(3):211–220. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0909169. PubMed PMID: 20647198. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stone JH, Merkel PA, Spiera R, Seo P, Langford CA, Hoffman GS, Kallenberg CG, St Clair EW, Turkiewicz A, Tchao NK, Webber L, Ding L, Sejismundo LP, Mieras K, Weitzenkamp D, Ikle D, Seyfert-Margolis V, Mueller M, Brunetta P, Allen NB, Fervenza FC, Geetha D, Keogh KA, Kissin EY, Monach PA, Peikert T, Stegeman C, Ytterberg SR, Specks U. RAVE-ITN Research Group. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for ANCA-associated vasculitis. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(3):221–232. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0909905. PubMed PMID: 20647199. Pubmed Central PMCID: 3137658. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jones RB, Ferraro AJ, Chaudhry AN, Brogan P, Salama AD, Smith KG, Savage CO, Jayne DR. A multicenter survey of rituximab therapy for refractory antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(7):2156–2168. doi: 10.1002/art.24637. PubMed PMID: 19565480. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Guerry MJ, Brogan P, Bruce IN, D’Cruz DP, Harper L, Luqmani R, Pusey CD, Salama AD, Scott DG, Savage CO, Watts RA, Jayne DR. Recommendations for the use of rituximab in anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis. Rheumatology. 2012;51(4):634–643. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ker150. PubMed PMID: 21613248. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

