Overexpression of CIP2A is an independent prognostic indicator in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its depletion suppresses cell proliferation and tumor growth
- PMID: 24884612
- PMCID: PMC4046003
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-111
Overexpression of CIP2A is an independent prognostic indicator in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its depletion suppresses cell proliferation and tumor growth
Abstract
Background: Cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A (CIP2A) is an oncoprotein that acts as a prognostic marker for several human malignancies. In this study, we investigated the clinical significance of CIP2A and its function in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC).
Methods: Quantitative RT-PCR, western blot, and immunohistochemistry analyses were used to quantify CIP2A expression in NPC cell lines and clinical samples. Kaplan-Meier curves were used to estimate the association between CIP2A expression and patient survival. The functional role of CIP2A in NPC cell lines was evaluated by small interfering RNA-mediated depletion of the protein followed by analyses of cell proliferation and xenograft growth.
Results: CIP2A levels were upregulated in NPC cell lines and clinical samples at both the mRNA and protein levels (P < 0.01). Patients with high CIP2A expression had poorer overall survival (HR, 1.98; 95% CI, 1.16-3.34; P = 0.01) and poorer disease-free survival (HR, 1.68; 95% CI, 1.07-2.62; P = 0.02) rates than patients with low CIP2A expression. In addition, CIP2A expression status was an independent prognostic indicator for NPC patients. The depletion of CIP2A expression inhibited c-Myc protein expression in NPC cell lines, suppressed cell viability, colony formation, and anchorage-independent growth in vitro, and inhibited xenograft tumor growth in vivo.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate that high CIP2A expression in patients was associated with poor survival in NPC, and depletion of CIP2A expression inhibited NPC cell proliferation and tumor growth. Thus, these results warrant further investigation of CIP2A as a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of NPC.
Figures
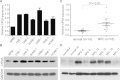
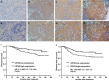


Similar articles
-
MYC-dependent regulation and prognostic role of CIP2A in gastric cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009 Jun 3;101(11):793-805. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djp103. Epub 2009 May 26. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009. PMID: 19470954
-
Effect of CIP2A and its mechanism of action in the malignant biological behavior of colorectal cancer.Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Apr 22;18(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00545-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 32321509 Free PMC article.
-
CIP2A mediates prostate cancer progression via the c-Myc signaling pathway.Tumour Biol. 2015 Jun;36(6):4777-83. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3129-4. Epub 2015 Jan 31. Tumour Biol. 2015. Retraction in: Tumour Biol. 2017 Apr 20. doi: 10.1007/s13277-017-5487-6. PMID: 25636449 Retracted.
-
Oncogenic nexus of cancerous inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A (CIP2A): an oncoprotein with many hands.Oncotarget. 2014 Jul 15;5(13):4581-602. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2127. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25015035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of CIP2A in cancer: A review and update.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Dec;96:626-633. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.146. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 29035828 Review.
Cited by
-
High expression of Talin-1 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2015 Apr 30;15:332. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1351-5. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25925041 Free PMC article.
-
CPVL suppresses metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Dec;149(18):16473-16488. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05340-7. Epub 2023 Sep 15. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37712963 Free PMC article.
-
TIPRL1 and its ATM-dependent phosphorylation promote radiotherapy resistance in head and neck cancer.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024 Jun;47(3):793-818. doi: 10.1007/s13402-023-00895-6. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024. PMID: 37971644
-
CIP2A overexpression in Taiwanese oral cancer patients.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Apr 5;11:2589-2594. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S201154. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31114325 Free PMC article.
-
Cancerous Inhibitor of Protein Phosphatase 2A as a Molecular Marker for Aggressiveness and Survival in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.J Cancer Prev. 2020 Mar 30;25(1):21-26. doi: 10.15430/JCP.2020.25.1.21. J Cancer Prev. 2020. PMID: 32266176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cho WC. Cancer report of Asian-Pacific region 2010. Asian Pacific Organization for Cancer Prevention; 2010. Most common cancers in Asia-Pacific region: nasopharyngeal carcinoma; pp. 284–289.
-
- Lai SZ, Li WF, Chen L, Luo W, Chen YY, Liu LZ, Sun Y, Lin AH, Liu MZ, Ma J. How does intensity-modulated radiotherapy versus conventional two-dimensional radiotherapy influence the treatment results in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;80:661–668. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.03.024. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Sun Y, Liang SB, Zong JF, Li WF, Chen M, Chen L, Mao YP, Tang LL, Guo Y, Lin AH, Liu MZ, Ma J. Progress report of a randomized trial comparing long-term survival and late toxicity of concurrent chemoradiotherapy with adjuvant chemotherapy versus radiotherapy alone in patients with stage III to IVB nasopharyngeal carcinoma from endemic regions of China. Cancer. 2013;119:2230–2238. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28049. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

