Free posterior tibial flap reconstruction for hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 24884631
- PMCID: PMC4038592
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7819-12-163
Free posterior tibial flap reconstruction for hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this article was to determine outcomes in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the hypopharynx (SCCHP) in whom the free posterior tibial flap was used for primary reconstruction of hypopharynx defects after cancer resection.
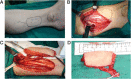
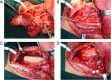
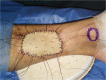
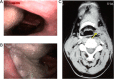
Subjects and methods: Between August 2009 and February 2012, 10 patients with SCCHP underwent posterior tibial flap reconstruction for hypopharynx defects. The corresponding clinical data were retrospectively collected and analyzed.
Results: Despite the multistep and time-consuming procedure, the posterior tibial flap survival rate was 100%. Operation-induced complications did not occur in four patients. Six patients developed postoperative hypoproteinemia, four patients developed postoperative pulmonary infections, and four patients developed pharyngeal fistula. The pharyngeal and laryngeal functions of all patients were preserved.
Conclusion: Our experience demonstrates that the posterior tibial flap is a safe and reliable choice for the reconstruction of hypopharynx defects.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Free flap combined with pectoralis major flap for reconstruction after total laryngopharyngectomy in patients with advanced hypopharyngeal carcinoma.Acta Otolaryngol. 2016 Aug;136(8):841-6. doi: 10.3109/00016489.2016.1164891. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Acta Otolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 27066846
-
[Functional long-term results following hemipharyngo-hemilaryngectomy and microvascular reconstruction using the radial forearm flap].Laryngorhinootologie. 2002 Mar;81(3):233-42. doi: 10.1055/s-2002-25036. Laryngorhinootologie. 2002. PMID: 11967777 German.
-
Free jejunal graft for reconstruction of defects in the hypopharynx and cervical esophagus following the cancer resections.J Gastrointest Surg. 2009 Jul;13(7):1368-72. doi: 10.1007/s11605-009-0877-8. Epub 2009 Mar 31. J Gastrointest Surg. 2009. PMID: 19333658
-
Reconstruction of the hypopharynx after surgical treatment of squamous cell carcinoma.J Chin Med Assoc. 2009 Jul;72(7):351-5. doi: 10.1016/S1726-4901(09)70386-7. J Chin Med Assoc. 2009. PMID: 19581140 Review.
-
Preservation of the larynx after resection of a carcinoma of the posterior wall of the hypopharynx: versatility of a free flap patch graft.Head Neck. 1997 Mar;19(2):137-42. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0347(199703)19:2<137::aid-hed9>3.0.co;2-5. Head Neck. 1997. PMID: 9059872 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of xenogenic acellular dermal matrix in reconstruction of oncological hypopharyngeal defects.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Dec;273(12):4391-4396. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-4088-0. Epub 2016 May 10. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 27164947
-
Comparison between free posterior tibial flap and free radial forearm flap for head and neck reconstruction: an anatomical study and a retrospective comparative cohort study.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Nov;10(22):1231. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-5426. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36544636 Free PMC article.
-
Application of prolonged submental perforator flap to repair the postoperative defect of upper airway malignancy.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Dec;280(12):5507-5518. doi: 10.1007/s00405-023-08131-5. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 37530858 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction of cervical and upper thoracic esophagus with a free posterior tibial artery perforator flap: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Nov 13;99(46):e22617. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022617. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33181646 Free PMC article.
-
Free posterior tibial artery perforator flap for 2-stage tracheal reconstruction in patients after resection of well-differentiated thyroid carcinoma invading the trachea.Head Neck. 2019 Jul;41(7):2249-2255. doi: 10.1002/hed.25675. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Head Neck. 2019. PMID: 30729609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murakami Y, Ikari T, Haraguchi S. Excision level and indication for contralateral neck dissection in hypopharyngeal cancer surgery. Auris Nasus Larynx. 1985;12(Suppl 2):S36–S40. - PubMed
-
- Bradley PJ. Multidisciplinary clinical approach to the management of head and neck cancer. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;269:2451–2454. - PubMed
-
- Plouin-Gaudon I, Lengele B, Desuter G. Conservation laryngeal surgery for selected pyriform sinus cancer. Eur J SurgOncol. 2004;30:1123–1130. - PubMed
-
- Joo YH, Sun DI, Cho KJ. Fasciocutaneous free flap reconstruction for squamous cell carcinoma of the hypopharynx. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;268:289–294. - PubMed
-
- Harii K, Ebihara S, Ono I. Pharyngoesophageal reconstruction using a fabricated forearm free flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1985;75:463–476. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

