Role of inflammation in previously untreated macular edema with branch retinal vein occlusion
- PMID: 24884703
- PMCID: PMC4032564
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2415-14-67
Role of inflammation in previously untreated macular edema with branch retinal vein occlusion
Abstract
Background: The association of inflammatory factors and the aqueous flare value with macular edema in branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO) patients remains unclear. The relationship between the aqueous flare value and the vitreous fluid levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), interleukin (IL)-6, monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP)-1, soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (sICAM-1), and soluble VEGF receptor-2 (sVEGFR-2) was evaluated to investigate the role of inflammation in BRVO associated with macular edema. Aqueous flare values and the vitreous levels of VEGF, IL-6, MCP-1, sICAM-1, and sVEGFR-2 were compared between previously untreated patients with BRVO and patients with macular hole (MH).
Methods: Vitreous samples were obtained from 45 patients during vitreoretinal surgery (28 patients with BRVO and 17 with MH), and the levels of VEGF, IL-6, MCP-1, sICAM-1, and sVEGFR-2 were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Retinal ischemia was evaluated by measuring the area of capillary non-perfusion using fluorescein angiography and the Scion Image program. Aqueous flare values were measured with a laser flare meter and macular edema was examined by optical coherence tomography.
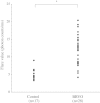
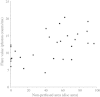
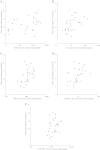
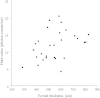
Results: The median aqueous flare value was significantly higher in the BRVO group (12.1 photon counts/ms) than in the MH group (4.5 photon counts/ms, P < 0.001). There were significant correlations between the aqueous flare value and the vitreous levels of VEGF, IL-6, MCP-1, and sICAM-1 in the BRVO group (ρ = 0.54, P = 0.005; ρ = 0.56, P = 0.004; ρ = 0.52, P = 0.006; and ρ = 0.47, P = 0.015, respectively). The aqueous flare value was also significantly correlated with the foveal thickness in the BRVO group (ρ = 0.40, P = 0.037).
Conclusions: Inflammation may induce an increase of vascular permeability and disrupt the blood-aqueous barrier via release of inflammatory factors (VEGF, IL-6, MCP-1, and sICAM-1) in BRVO patients with macular edema.
Figures
References
-
- Pai SA, Shetty R, Vijayan PB, Venkatasubramaniam G, Yadav NK, Shetty BK, Babu RB, Narayana KM. Clinical, anatomic, and electrophysiologic evaluation following intravitreal bevacizumab for macular edema in retinal vein occlusion. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007;143:601–606. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2006.12.037. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Campochiaro PA, Hafiz G, Shah SM, Nguyen QD, Ying H, Do DV, Quinlan E, Zimmer-Galler I, Haller JA, Solomon SD, Sung JU, Hadi Y, Janjua KA, Jawed N, Choy DF, Arron JR. Ranibizumab for macular edema due to retinal vein occlusions: implication of VEGF as a critical stimulator. Mol Ther. 2008;16:791–799. doi: 10.1038/mt.2008.10. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Campochiaro PA, Heier JS, Feiner L, Gray S, Saroj N, Rundle AC, Murahashi WY, Rubio RG. Ranibizumab for macular edema following branch retinal vein occlusion: six-month primary end point results of a phase III study. Ophthalmology. 2010;117:1102–1112 e1. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2010.02.021. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Noma H, Funatsu H, Yamasaki M, Tsukamoto H, Mimura T, Sone T, Jian K, Sakamoto I, Nakano K, Yamashita H, Minamoto A, Mishima HK. Pathogenesis of macular edema with branch retinal vein occlusion and intraocular levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-6. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005;140:256–261. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

