A polymorphism in the DNA repair domain of APEX1 is associated with the radiation-induced pneumonitis risk among lung cancer patients after radiotherapy
- PMID: 24884729
- PMCID: PMC4112388
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20140093
A polymorphism in the DNA repair domain of APEX1 is associated with the radiation-induced pneumonitis risk among lung cancer patients after radiotherapy
Abstract
Objective: To examine the association of tag single nucleotide polymorphisms (tagSNPs) (rs1130409, rs1760944, rs2307486 and rs3136817) in APEX1 with the risk of severe radiation-induced pneumonitis (RP) after radiotherapy among Han Chinese patients with lung cancer.
Methods: A total of 168 patients with lung cancer who were receiving radiotherapy were prospectively recruited. RP was evaluated according to the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. A case-control study was performed. The case group included patients with RP grade of ≥3, while the control group comprised patients with RP grades <3. Four tagSNPs of APEX1 were genotyped in 126 patients with complete follow-up by multi-SNaPshot® (Genesky Biotechnologies Inc., Shanghai, China) genotyping assays. RESULTS were assessed by a logistic regression model for RP risk and Mantal-Cox log-rank test for the cumulative RP probability by the genotypes.
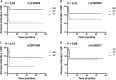
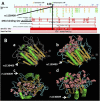
Results: rs1130409 was associated with severe RP. GT genotype of rs1130409 was significantly higher in patients with RP than in those of the control group [68.8% vs 41.8%; p = 0.025; resulting odds ratio (OR), 5.98]. Patients with lung cancer bearing the G allele had a 5.83-fold higher risk of RP than those with the wild TT genotype [OR = 5.83; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.27-26.90; p = 0.024], and this was further confirmed by the binary regression adjusted by some confounding factors, including Karnofsky performance scale, concurrent chemotherapy-radiotherapy and lung volume receiving >30 Gy (OR = 6.96; 95% CI, 1.36-35.77; p = 0.02). rs1130409 was also associated with the time to occurrence of severe RP (p = 0.04). Three-dimensional model APEX1 protein showed that rs1130409 is located in the random coil structure corresponding to the DNA repair function region.
Advances in knowledge: rs1130409 of APEX1 can be a predictor of RP grades ≥3 among patients with lung cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of APEX1 and OGG1 gene polymorphisms with breast cancer risk among Han women in the Gansu Province of China.BMC Med Genet. 2018 May 2;19(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12881-018-0578-9. BMC Med Genet. 2018. PMID: 29720094 Free PMC article.
-
Functional polymorphisms of base excision repair genes XRCC1 and APEX1 predict risk of radiation pneumonitis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with definitive radiation therapy.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011 Nov 1;81(3):e67-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.11.079. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011. PMID: 21420246 Free PMC article.
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism at rs1982073:T869C of the TGFbeta 1 gene is associated with the risk of radiation pneumonitis in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer treated with definitive radiotherapy.J Clin Oncol. 2009 Jul 10;27(20):3370-8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.20.6763. Epub 2009 Apr 20. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19380441 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Repair Genetics and the Risk of Radiation Pneumonitis in Patients With Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2024 Jul;36(7):e182-e196. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2024.03.019. Epub 2024 Mar 24. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2024. PMID: 38653664
-
Association between the APEX1 Asp148Glu polymorphism and prostate cancer, especially among Asians: a new evidence-based analysis.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 9;7(32):52530-52540. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9693. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27248666 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Associations between polymorphisms in genes of base excision repair pathway and lung cancer risk.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Apr;9(4):2780-2800. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2020.02.44. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117636 Free PMC article.
-
Association of APEX1 and OGG1 gene polymorphisms with breast cancer risk among Han women in the Gansu Province of China.BMC Med Genet. 2018 May 2;19(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12881-018-0578-9. BMC Med Genet. 2018. PMID: 29720094 Free PMC article.
-
miR-296-3p targets APEX1 to suppress cell migration and invasion of non-small-cell lung cancer.Oncol Lett. 2019 Sep;18(3):2612-2618. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10572. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31402954 Free PMC article.
-
APEX1 Polymorphisms and Neuroblastoma Risk in Chinese Children: A Three-Center Case-Control Study.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Jun 25;2019:5736175. doi: 10.1155/2019/5736175. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31341530 Free PMC article.
-
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in APE1, hOGG1, RAD51 Genes and their Association with Radiotherapy Induced Toxicity among Head and Neck Cancer Patients.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024 Aug 1;25(8):2645-2654. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2024.25.8.2645. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2024. PMID: 39205561 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roach M3rd, Gandara DR, Yuo HS, Swift PS, Kroll S, Shrieve DC, et al. . Radiation pneumonitis following combined modality therapy for lung cancer: analysis of prognostic factors. J Clin Oncol 1995; 13: 2606–12. - PubMed
-
- Provatopoulou X, Athanasiou E, Gounaris A. Predictive markers of radiation pneumonitis. Anticancer Res 2008; 28: 2421–32. - PubMed
-
- Koga K, Kusumoto S, Watanabe K, Nishikawa K, Harada K, Ebihara H. Age factor relevant to the development of radiation pneumonitis in radiotherapy of lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1988; 14: 367–71. - PubMed
-
- Kong FM, Ten Haken R, Eisbruch A, Lawrence TS. Non-small cell lung cancer therapy-related pulmonary toxicity: an update on radiation pneumonitis and fibrosis. Semin Oncol 2005; 32: S42–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

