Whole brain radiotherapy plus simultaneous in-field boost with image guided intensity-modulated radiotherapy for brain metastases of non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 24884773
- PMCID: PMC4035738
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-9-117
Whole brain radiotherapy plus simultaneous in-field boost with image guided intensity-modulated radiotherapy for brain metastases of non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) plus sequential focal radiation boost is a commonly used therapeutic strategy for patients with brain metastases. However, recent reports on WBRT plus simultaneous in-field boost (SIB) also showed promising outcomes. The objective of present study is to retrospectively evaluate the efficacy and toxicities of WBRT plus SIB with image guided intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IG-IMRT) for inoperable brain metastases of NSCLC.
Methods: Twenty-nine NSCLC patients with 87 inoperable brain metastases were included in this retrospective study. All patients received WBRT at a dose of 40 Gy/20 f, and SIB boost with IG-IMRT at a dose of 20 Gy/5 f concurrent with WBRT in the fourth week. Prior to each fraction of IG-IMRT boost, on-line positioning verification and correction were used to ensure that the set-up errors were within 2 mm by cone beam computed tomography in all patients.
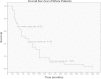
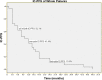
Results: The one-year intracranial control rate, local brain failure rate, and distant brain failure rate were 62.9%, 13.8%, and 19.2%, respectively. The two-year intracranial control rate, local brain failure rate, and distant brain failure rate were 42.5%, 30.9%, and 36.4%, respectively. Both median intracranial progression-free survival and median survival were 10 months. Six-month, one-year, and two-year survival rates were 65.5%, 41.4%, and 13.8%, corresponding to 62.1%, 41.4%, and 10.3% of intracranial progression-free survival rates. Patients with Score Index for Radiosurgery in Brain Metastases (SIR) >5, number of intracranial lesions <3, and history of EGFR-TKI treatment had better survival. Three lesions (3.45%) demonstrated radiation necrosis after radiotherapy. Grades 2 and 3 cognitive impairment with grade 2 radiation leukoencephalopathy were observed in 4 (13.8%) and 4 (13.8%) patients. No dosimetric parameters were found to be associated with these late toxicities. Patients received EGFR-TKI treatment had higher incidence of grades 2-3 cognitive impairment with grade 2 leukoencephalopathy.
Conclusions: WBRT plus SIB with IG-IMRT is a tolerable and effective treatment for NSCLC patients with inoperable brain metastases. However, the results of present study need to be examined by the prospective investigations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Whole Brain Irradiation and Hypo-fractionation Radiotherapy for the Metastases in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2016 Apr 20;19(4):224-9. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2016.04.08. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27118651 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Whole-brain radiotherapy plus sequential or simultaneous integrated boost for the treatment of a limited number of brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer: A single-institution study.Cancer Med. 2020 Jan;9(1):238-246. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2696. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 31749325 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal avoidance with volumetric modulated arc therapy in melanoma brain metastases - the first Australian experience.Radiat Oncol. 2013 Mar 18;8:62. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-8-62. Radiat Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23497418 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Brain Radiotherapy Simultaneous Integrated Boost Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy Combined With Anlotinib in the Treatment of Brain Metastases.Cancer Control. 2025 Jan-Dec;32:10732748251319489. doi: 10.1177/10732748251319489. Cancer Control. 2025. PMID: 39951682 Free PMC article.
-
Brain metastases in patients with oncogenic-driven non-small cell lung cancer: Pros and cons for early radiotherapy.Cancer Treat Rev. 2021 Nov;100:102291. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102291. Epub 2021 Sep 11. Cancer Treat Rev. 2021. PMID: 34587557 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of piecewise VMAT technique to whole-brain radiotherapy with simultaneous integrated boost for multiple metastases.Radiat Oncol. 2022 May 7;17(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13014-022-02059-6. Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35526019 Free PMC article.
-
[Whole Brain Irradiation and Hypo-fractionation Radiotherapy for the Metastases in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2016 Apr 20;19(4):224-9. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2016.04.08. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27118651 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Whole-Brain Radiation Therapy With Simultaneous Integrated Boost Versus Whole-Brain Radiation Therapy Plus Stereotactic Radiosurgery for the Treatment of Brain Metastasis From Lung Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 5;11:631422. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.631422. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33747953 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR as a Target for Glioblastoma Treatment: An Unfulfilled Promise.CNS Drugs. 2017 Sep;31(9):723-735. doi: 10.1007/s40263-017-0456-6. CNS Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28791656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modern Radiation Therapy for the Management of Brain Metastases From Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Approaches and Future Directions.Front Oncol. 2021 Nov 2;11:772789. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.772789. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34796118 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mujoomdar A, Austin JH, Malhotra R, Powell CA, Pearson GD, Shiau MC, Raftopoulos H. Clinical predictors of metastatic disease to the brain from non-small cell lung carcinoma: primary tumor size, cell type, and lymph node metastases. Radiology. 2007;242:882–888. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2423051707. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

