Enhancement of gefitinib-induced growth inhibition by Marsdenia tenacissima extract in non-small cell lung cancer cells expressing wild or mutant EGFR
- PMID: 24884778
- PMCID: PMC4040364
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-165
Enhancement of gefitinib-induced growth inhibition by Marsdenia tenacissima extract in non-small cell lung cancer cells expressing wild or mutant EGFR
Abstract
Background: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) expressed high levels of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Gefitinib (Iressa) has demonstrated clinical efficacy in NSCLC patients harboring EGFR mutations or refractory to chemotherapy. However, most of NSCLC patients are with wild type EGFR, and showed limited response to gefitinib. Therefore, to develop new effective therapeutic interventions for NSCLC is still required. Our previous study showed Marsdenia tenacissima extract (MTE) restored gefitinib efficacy in the resistant NSCLC cells, but whether MTE acts in the gefitinib-sensitive NSCLC cells is the same as it in the resistant one is unknown.
Methods: Dose response curves for gefitinib and MTE were generated for two sensitive NSCLC cell lines with mutant or wild type EGFR status. Three different sequential combinations of MTE and gefitinib on cell growth were evaluated using IC50 and Combination Index approaches. The flow cytometric method was used to detect cell apoptosis and cell cycle profile. The impact of MTE combined with gefitinib on cell molecular network response was studied by Western blotting.
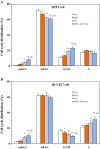
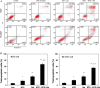
Results: Unlike in the resistant NSCLC cells, our results revealed that low cytotoxic dose of MTE (8 mg/ml) combined gefitinib with three different schedules synergistically or additively enhanced the growth inhibition of gefitinib. Among which, MTE→MTE+gefitinib treatment was the most effective one. MTE markedly prompted cell cycle arrest and apoptosis caused by gefitinib both in EGFR mutant (HCC827) and wild type of NSCLC cells (H292). The Western blotting results showed that MTE→MTE+gefitinib treatment further enhanced the suppression of gefitinib on cell growth and apoptosis pathway such as ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt/mTOR. This combination also blocked the activation of EGFR and c-Met which have cross-talk with each other. Unlike in gefitinib-resistant NSCLC cells, MTE alone also demonstrated certain unexpected modulation on EGFR related cell signal pathways in the sensitive cells.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that MTE is a promising herbal medicine to improve gefitinib efficacy in NSCLC regardless of EGFR status. However, why MTE acted differently between gefitinib-sensitive and -resistant NSCLC cells needs a further research.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Marsdenia tenacissima extract restored gefitinib sensitivity in resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells.Lung Cancer. 2012 Jan;75(1):30-7. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2011.06.001. Epub 2011 Jul 16. Lung Cancer. 2012. PMID: 21757251
-
Marsdenia tenacissima extract enhances gefitinib efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer xenografts.Phytomedicine. 2015 May 15;22(5):560-7. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2015.03.001. Epub 2015 Mar 27. Phytomedicine. 2015. PMID: 25981922
-
Chemotherapy-induced epidermal growth factor receptor activation determines response to combined gefitinib/chemotherapy treatment in non-small cell lung cancer cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2006 May;5(5):1154-65. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0446. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006. PMID: 16731747
-
[Progress in Palliative Care Benefit of Elderly Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2015 Jul;18(7):462-8. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2015.07.11. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26182873 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Why Iressa failed: toward novel use of kinase inhibitors (outlook).Cancer Biol Ther. 2003 Mar-Apr;2(2):137-40. doi: 10.4161/cbt.2.2.286. Cancer Biol Ther. 2003. PMID: 12750551 Review.
Cited by
-
C21 Fraction Refined from Marsdenia tenacissima-Induced Apoptosis is Enhanced by Suppression of Autophagy in Human Gastric Cell Lines.ACS Omega. 2020 Sep 24;5(39):25156-25163. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c02748. eCollection 2020 Oct 6. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 33043194 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxicity of anti-tumor herbal Marsdeniae tenacissimae extract on erythrocytes.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017 Jul;18(7):597-604. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1600228. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017. PMID: 28681584 Free PMC article.
-
Marsdenia tenacissimae extraction (MTE) inhibits the proliferation and induces the apoptosis of human acute T cell leukemia cells through inactivating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway via PTEN enhancement.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 13;7(50):82851-82863. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12654. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27756877 Free PMC article.
-
Marsdeniae tenacissima extract-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis in hepatoma carcinoma cells is mediated through the p53/nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Sep;14(3):2477-2484. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4833. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28962183 Free PMC article.
-
The Antitumor Activities of Marsdenia tenacissima.Front Oncol. 2018 Oct 23;8:473. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00473. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30406035 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mendelsohn J. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor for cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:1s–13s. - PubMed
-
- Habib AA, Chun SJ, Neel BG, Vartanian T. Increased expression of epidermal growth factor receptor induces sequestration of extracellular signal-related kinases and selective attenuation of specific epidermal growth factor-mediated signal transduction pathways. Mol Cancer Res. 2003;1:219–233. - PubMed
-
- Veale D, Kerr N, Gibson GJ, Harris AL. Characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor in primary human non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 1989;49:1313–1317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

