Interleukin 32γ (IL-32γ) is highly expressed in cutaneous and mucosal lesions of American Tegumentary Leishmaniasis patients: association with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and IL-10
- PMID: 24884781
- PMCID: PMC4026597
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-249
Interleukin 32γ (IL-32γ) is highly expressed in cutaneous and mucosal lesions of American Tegumentary Leishmaniasis patients: association with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and IL-10
Abstract
Background: The interleukin 32 (IL-32) is a proinflammatory cytokine produced by immune and non-immune cells. It can be induced during bacterial and viral infections, but its production was never investigated in protozoan infections. American Tegumentary Leishmaniasis (ATL) is caused by Leishmania protozoan leading to cutaneous, nasal or oral lesions. The aim of this study was to evaluate the expression of IL-32 in cutaneous and mucosal lesions as well as in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) exposed to Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis.
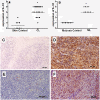
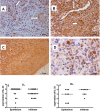
Methods: IL-32, tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and IL-10 protein expression was evaluated by immunohistochemistry in cutaneous, mucosal lesions and compared to healthy specimens. The isoforms of IL-32α, β, δ, γ mRNA, TNF mRNA and IL-10 mRNA were assessed by qPCR in tissue biopsies of lesions and healthy skin and mucosa. In addition, PBMC from healthy donors were cultured with amastigotes of L. (V.) braziliensis. In lesions, the parasite subgenus was identified by PCR-RFLP.
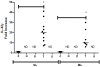
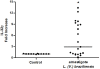
Results: We showed that the mRNA expression of IL-32, in particular IL-32γ was similarly up-regulated in lesions of cutaneous (CL) or mucosal (ML) leishmaniasis patients. IL-32 protein was produced by epithelial, endothelial, mononuclear cells and giant cells. The IL-32 protein expression was associated with TNF in ML but not in CL. IL-32 was not associated with IL-10 in both CL and ML. Expression of TNF mRNA was higher in ML than in CL lesions, however levels of IL-10 mRNA were similar in both clinical forms. In all lesions in which the parasite was detected, L. (Viannia) subgenus was identified. Interestingly, L. (V.) braziliensis induced only IL-32γ mRNA expression in PBMC from healthy individuals.
Conclusions: These data suggest that IL-32 plays a major role in the inflammatory process caused by L. (Viannia) sp or that IL-32 is crucial for controlling the L. (Viannia) sp infection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Critical Overview of Interleukin 32 in Leishmaniases.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 3;13:849340. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.849340. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35309341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-32γ promotes the healing of murine cutaneous lesions caused by Leishmania braziliensis infection in contrast to Leishmania amazonensis.Parasit Vectors. 2017 Jul 14;10(1):336. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2268-4. Parasit Vectors. 2017. PMID: 28709468 Free PMC article.
-
The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of human tegumentary leishmaniasis.Cytokine. 2014 Apr;66(2):127-32. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2013.12.016. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Cytokine. 2014. PMID: 24485388 Free PMC article.
-
A recombinant Leishmania antigen that stimulates human peripheral blood mononuclear cells to express a Th1-type cytokine profile and to produce interleukin 12.J Exp Med. 1995 Apr 1;181(4):1527-37. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.4.1527. J Exp Med. 1995. PMID: 7699334 Free PMC article.
-
Protection and Pathology in Leishmania braziliensis Infection.Pathogens. 2022 Apr 14;11(4):466. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11040466. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35456141 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Critical Overview of Interleukin 32 in Leishmaniases.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 3;13:849340. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.849340. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35309341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor α Therapeutics Differentially Affect Leishmania Infection of Human Macrophages.Front Immunol. 2018 Jul 31;9:1772. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01772. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30108591 Free PMC article.
-
IL-32 as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target in skin inflammation.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 1;14:1264236. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1264236. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37727785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipophosphoglycan From Dermotropic New World Leishmania Upregulates Interleukin-32 and Proinflammatory Cytokines Through TLR4 and NOD2 Receptors.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Mar 23;12:805720. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.805720. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35402314 Free PMC article.
-
Host SUMOylation Pathway Negatively Regulates Protective Immune Responses and Promotes Leishmania donovani Survival.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jun 6;12:878136. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.878136. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35734580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dahl CA, Schall RP, He HL, Cairns JS. Identification of a novel gene expressed in activated natural killer cells and T cells. J Immunol. 1992;14:597–603. - PubMed
-
- Kim SH, Han SY, Azam T, Yoon DY, Dinarello CA. Interleukin-32: a cytokine and inducer of TNF alpha. Immunity. 2005;14:131–142. - PubMed
-
- Goda C, Kanaji T, Kanaji S, Tanaka G, Arima K, Ohno S, Izuhara K. Involvement of IL-32 in activation-induced cell death in T cells. Int Immunol. 2006;14:233–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

