A pilot three-month sitagliptin treatment increases serum adiponectin level in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus--a randomized controlled trial START-J study
- PMID: 24884787
- PMCID: PMC4049487
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-13-96
A pilot three-month sitagliptin treatment increases serum adiponectin level in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus--a randomized controlled trial START-J study
Abstract
Background: The dipeptidyl-peptidase-IV (DPP-4) inhibitors, including sitagliptin, are used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Adiponectin, an adipocyte-derived circulating protein, has anti-atherosclerotic and anti-diabetic properties and is effectively elevated in bloodstream by thiazolidinediones, an insulin sensitizer. However, the effect of sitagliptin treatment on serum adiponectin level in T2DM has not fully elucidated in Japanese T2DM patients. The aim of the present study was to examine the effect of sitagliptin treatment on serum adiponectin levels in T2DM subjects.
Methods: Twenty-six consecutive Japanese T2DM outpatients were recruited between April 2011 and March 2013, and randomized into the control (conventional treatment, n = 10) group and sitagliptin treatment group (n = 16). Serum adiponectin was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
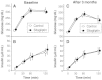
Results: Indices of glycemic control, such as hemoglobin A1c, glycated albumin, and 1.5-anhydro-D-glucitol, were significantly improved after the three-month treatment in both the control and sitagliptin groups. Serum adiponectin level was significantly increased in sitagliptin group from 6.7 ± 0.8 to 7.4 ± 1.0 μg/mL without change of body mass index (p = 0.034), while serum adiponectin level was not altered in the control group (p = 0.601).
Conclusion: In Japanese T2DM patients, serum adiponectin level was elevated by three-month treatment with sitagliptin without change of body weight.
Trial registration: UMIN000004721.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of sitagliptin on glycemic control and beta cell function in Japanese patients given basal-supported oral therapy for type 2 diabetes.Endocr J. 2014;61(12):1213-20. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ14-0194. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Endocr J. 2014. PMID: 25231694
-
Add-on therapy with the DPP-4 inhibitor sitagliptin improves glycemic control in insulin-treated Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Endocr J. 2013;60(6):733-42. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.ej12-0293. Epub 2013 Feb 2. Endocr J. 2013. PMID: 23386390
-
Cotreatment with the α-glucosidase inhibitor miglitol and DPP-4 inhibitor sitagliptin improves glycemic control and reduces the expressions of CVD risk factors in type 2 diabetic Japanese patients.Metabolism. 2014 Jun;63(6):746-53. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.12.014. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Metabolism. 2014. PMID: 24559582 Clinical Trial.
-
Incretin mimetics and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in clinical trials for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008 Jun;17(6):845-53. doi: 10.1517/13543784.17.6.845. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18491986 Review.
-
Combination therapy with DPP-4 inhibitors and pioglitazone in type 2 diabetes: theoretical consideration and therapeutic potential.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2008;4(6):1221-7. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.s3374. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2008. PMID: 19337535 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on serum adiponectin: a meta-analysis.Lipids Health Dis. 2016 Nov 23;15(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0372-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2016. PMID: 27881129 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of effects of sitagliptin and voglibose on left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes: results of the 3D trial.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015 Jun 19;14:83. doi: 10.1186/s12933-015-0242-z. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015. PMID: 26084668 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Significant Association of Serum Adiponectin and Creatine Kinase-MB Levels in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2017 Aug 1;24(8):793-803. doi: 10.5551/jat.38232. Epub 2017 Jan 17. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2017. PMID: 28100880 Free PMC article.
-
A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing the Effects of Sitagliptin and Glimepiride on Endothelial Function and Metabolic Parameters: Sapporo Athero-Incretin Study 1 (SAIS1).PLoS One. 2016 Oct 6;11(10):e0164255. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164255. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27711199 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
All-cause mortality of insulin plus dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in persons with type 2 diabetes.BMC Endocr Disord. 2019 Jan 5;19(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12902-018-0330-7. BMC Endocr Disord. 2019. PMID: 30611254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maeda N, Takahashi M, Funahashi T, Kihara S, Nishizawa H, Kishida K, Nagaretani H, Matsuda M, Komuro R, Ouchi N, Kuriyama H, Hotta K, Nakamura T, Shimomura I, Matsuzawa Y. PPARgamma ligands increase expression and plasma concentrations of adiponectin, an adipose-derived protein. Diabetes. 2001;50:2094–2099. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.50.9.2094. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kim Chung le T, Hosaka T, Yoshida M, Harada N, Sakaue H, Sakai T, Nakaya Y. Exendin-4, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, directly induces adiponectin expression through protein kinase A pathway and prevents inflammatory adipokine expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;390:613–618. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.10.015. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

