Nutlin-3 overcomes arsenic trioxide resistance and tumor metastasis mediated by mutant p53 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 24884809
- PMCID: PMC4046148
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-133
Nutlin-3 overcomes arsenic trioxide resistance and tumor metastasis mediated by mutant p53 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Arsenic trioxide has been demonstrated as an effective anti-cancer drug against leukemia and solid tumors both in vitro and in vivo. However, recent phase II trials demonstrated that single agent arsenic trioxide was poorly effective against hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which might be due to drug resistance.
Methods: Mutation detection of p53 gene in arsenic trioxide resistant HCC cell lines was performed. The therapeutic effects of arsenic trioxide and Nutlin-3 on HCC were evaluated both in vitro and in vivo. A series of experiments including MTT, apoptosis assays, co-Immunoprecipitation, siRNA transfection, lentiviral infection, cell migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchy-mal transition (EMT) assays were performed to investigate the underlying mechanisms.
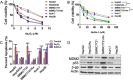
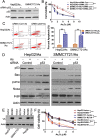
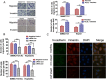
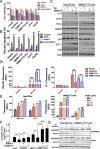
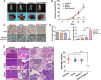
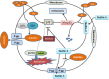
Results: The acquisition of p53 mutation contributed to arsenic trioxide resistance and enhanced metastatic potential of HCC cells. Mutant p53 (Mutp53) silence could re-sensitize HCC resistant cells to arsenic trioxide and inhibit the metastatic activities, while mutp53 overexpression showed the opposite effects. Neither arsenic trioxide nor Nutlin-3 could exhibit obvious effects against arsenic trioxide resistant HCC cells, while combination of them showed significant effects. Nutlin-3 can not only increase the intracellular arsenicals through inhibition of p-gp but also promote the p73 activation and mutp53 degradation mediated by arsenic trioxide. In vivo experiments indicated that Nutlin-3 can potentiate the antitumor activities of arsenic trioxide in an orthotopic hepatic tumor model and inhibit the metastasis to lung.
Conclusions: Acquisitions of p53 mutations contributed to the resistance of HCC to arsenic trioxide. Nutlin-3 could overcome arsenic trioxide resistance and inhibit tumor metastasis through p73 activation and promoting mutant p53 degradation mediated by arsenic trioxide.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MDM2 antagonist can inhibit tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma with different types of p53 in vitro.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011 Feb;26(2):371-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2010.06440.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21261729
-
Nutlin-3 cooperates with doxorubicin to induce apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through p53 or p73 signaling pathways.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2010 Oct;136(10):1597-604. doi: 10.1007/s00432-010-0817-8. Epub 2010 Feb 20. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20174822 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-539 suppresses tumor growth and tumorigenesis and overcomes arsenic trioxide resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.Life Sci. 2016 Dec 1;166:34-40. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.10.002. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27717846
-
Nanocarrier-based delivery of arsenic trioxide for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2022 Nov;17(26):2037-2054. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2022-0250. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2022. PMID: 36789952 Review.
-
Arsenic trioxide and neuroblastoma cytotoxicity.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2007 Feb;39(1):35-41. doi: 10.1007/s10863-006-9058-6. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2007. PMID: 17549641 Review.
Cited by
-
Low-dose Actinomycin-D treatment re-establishes the tumoursuppressive function of P53 in RELA-positive ependymoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 20;7(38):61860-61873. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11452. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27556362 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of mutant p53 in oral squamous cell carcinoma is correlated with the effectiveness of intra-arterial chemotherapy.Oncol Lett. 2015 Nov;10(5):2883-2887. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3651. Epub 2015 Aug 27. Oncol Lett. 2015. PMID: 26722257 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting p53 pathways: mechanisms, structures, and advances in therapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Mar 1;8(1):92. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01347-1. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 36859359 Free PMC article.
-
Super-enhancer-driven AJUBA is activated by TCF4 and involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Theranostics. 2020 Jul 11;10(20):9066-9082. doi: 10.7150/thno.45349. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32802179 Free PMC article.
-
Arsenic Trioxide Inhibits the Metastasis of Small Cell Lung Cancer by Blocking Calcineurin-Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cells (NFAT) Signaling.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Mar 26;25:2228-2237. doi: 10.12659/MSM.913091. Med Sci Monit. 2019. Retraction in: Med Sci Monit. 2024 Jan 30;30:e943940. doi: 10.12659/MSM.943940. PMID: 30913205 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Vahter M. Mechanisms of arsenic biotransformation. Toxicology. 2002;181–182:211–217. - PubMed
-
- Lin CC, Hsu C, Hsu CH, Hsu WL, Cheng AL, Yang CH. Arsenic trioxide in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase II trial. Invest New Drugs. 2007;25(1):77–84. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Zhang M, Liu LX. The overexpression of multidrug resistance-associated proteins and Gankyrin contribute to arsenic trioxide resistance in liver and gastric cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2009;22(1):73–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

