Phenolic contents, antioxidant and anticholinesterase potentials of crude extract, subsequent fractions and crude saponins from Polygonum hydropiper L
- PMID: 24884823
- PMCID: PMC4018186
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-145
Phenolic contents, antioxidant and anticholinesterase potentials of crude extract, subsequent fractions and crude saponins from Polygonum hydropiper L
Abstract
Background: We investigated Polygonum hydropiper L. (P. hydropiper) for phenolic contents, antioxidant, anticholinesterase activities, in an attempt to rationalize its use in neurological disorders.
Methods: Plant crude extract (Ph.Cr), its subsequent fractions: n-hexane (Ph.Hex), chloroform (Ph.Chf), ethyl acetate (Ph.EtAc), n-Butanol (Ph.Bt), aqueous (Ph.Aq) and saponins (Ph.Sp) were evaluated for 1,1-diphenyl,2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), 2,2-azinobis[3-ethylbenzthiazoline]-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) free radical scavenging potential. Further, acetylcholinesterase (AChE) & butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) inhibitory activities were performed using Ellman's assay. Moreover, total phenolic contents of plant extracts were determined and expressed in mg of gallic acid equivalent per gram of dry sample (mg GAE/g dry weight).
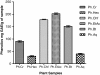
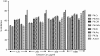
Results: Among different fractions, Ph.Cr (90.82), Ph.Chf (178.16), Ph.EtAc (203.44) and Ph.Bt (153.61) exhibited high phenolic contents. All fractions showed concentration dependent DPPH scavenging activity, with Ph.EtAc 71.33% (IC50 15 μg/ml), Ph.Bt 71.40% (IC50 3 μg/ml) and Ph.Sp 71.40% (IC50 35 μg/ml) were most potent. The plant extracts exhibited high ABTS scavenging ability i.e. Ph.Bt (91.03%), Ph.EtAc (90.56%), Ph.Sp (90.84%), Ph.Aq (90.56%) with IC50<0.01 μg/ml. All fractions showed moderate to high AChE inhibitory activity as; Ph.Cr, 86.87% (IC50 330 μg/ml), Ph.Hex, 87.49% (IC50 35 μg/ml), Ph.Chf, 84.76% (IC50 55 μg/ml), Ph.Sp, 87.58% (IC50 108 μg/ml) and Ph.EtAc 79.95% (IC50 310 μg/ml) at 1 mg/ml). Furthermore the BChE inhibitory activity was most prominent in Ph.Hex 90.30% (IC50 40 μg/ml), Ph.Chf 85.94% (IC50 215 μg/ml), Ph.Aq 87.62% (IC50 3 μg/ml) and Ph.EtAc 81.01% (IC50 395 μg/ml) fractions.
Conclusions: In this study, for the first time, we determined phenolic contents, isolated crude saponins, investigated antioxidant and anticholinestrase potential of P. hydropiper extracts. The results indicate that P. hydropiper is enriched with potent bioactive compounds and warrant further investigation by isolation and structural elucidation to find novel and affordable compounds for the treatment of various neurological disorders.
Figures

References
-
- Sharma R. Medicinal plants of India-An encyclopedia. Daya Publishing House, 110035 Delhi, India. 2003. pp. 46–47.
-
- Foster S, James AD. A field guide to medicinal plants: Eastern and central North America. Peterson Field Guide Series, 2nd edition, Houghton Mifflin Park Avenue, New York 10003. 1990. p. 241.
-
- Chevallier A. Dorling Kindersley London. London: Andrew DK Publishing; 1996. The encyclopedia of medicinal plants; p. 185. ISBN 9-780751-303148.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

