Unprecedented high insulin secretion in a healthy human subject after intravenous glucagon-like peptide-1: a case report
- PMID: 24885055
- PMCID: PMC4053292
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-326
Unprecedented high insulin secretion in a healthy human subject after intravenous glucagon-like peptide-1: a case report
Abstract
Background: The gut-derived incretin hormones, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and glucagon-like peptide-1, are released in response to ingestion of nutrients. Both hormones are highly insulinotropic in strictly glucose-dependent fashions and glucagon-like peptide-1 is often referred to as one of the most insulinotropic substances known.
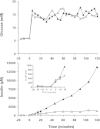
Case presentation: Plasma insulin and C-peptide concentrations were measured in a healthy Caucasian male (age: 53 years; body mass index: 28.6 kg/m2; fasting plasma glucose: 5.7 mM; 2 h plasma glucose value following 75 g-oral glucose tolerance test: 3.5 mM; glycated haemoglobin A1c: 5.5%) during glucagon (1 mg) and meal (2,370 kJ) tests, and during two 2 h 15 mM-hyperglycaemic clamps with continuous intravenous infusion of glucagon-like peptide-1 (1 pmol/kg/min) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (4 pmol/kg/min), respectively. Normal insulin and C-peptide responses were observed during meal test (peak concentrations: 300 and 3,278 pM) and glucagon test (peak concentrations: 250 and 2,483 pM). During the hyperglycaemic clamp with continuous intravenous infusion of GLP-1 the subject exhibited plasma insulin and C-peptide concentrations of 13,770 and 22,380 pM, respectively.
Conclusions: To our knowledge insulin and C-peptide concentrations of these magnitudes have never been reported. Thus, the present data support the view that glucagon-like peptide-1 is one of the most insulinotropic substances known.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Both GLP-1 and GIP are insulinotropic at basal and postprandial glucose levels and contribute nearly equally to the incretin effect of a meal in healthy subjects.Regul Pept. 2003 Jul 15;114(2-3):115-21. doi: 10.1016/s0167-0115(03)00111-3. Regul Pept. 2003. PMID: 12832099
-
Preserved incretin activity of glucagon-like peptide 1 [7-36 amide] but not of synthetic human gastric inhibitory polypeptide in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus.J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):301-7. doi: 10.1172/JCI116186. J Clin Invest. 1993. PMID: 8423228 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impaired incretin-induced amplification of insulin secretion after glucose homeostatic dysregulation in healthy subjects.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Apr;97(4):1363-70. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-2594. Epub 2012 Feb 8. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22319034 Clinical Trial.
-
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide: effects on insulin and glucagon secretion in humans.Dan Med J. 2016 Apr;63(4):B5230. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 27034187 Review.
-
On the role of the gut in diabetic hyperglucagonaemia.Dan Med J. 2017 Apr;64(4):B5340. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28385175 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic stimulation of GLP-1 and GIP protein with DPP-4 inhibitors for type-2 diabetes treatment.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2015 Mar 19;14:15. doi: 10.1186/s40200-015-0143-4. eCollection 2015. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2015. Retraction in: J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2016 Aug 30;15(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s40200-016-0256-4. PMID: 26473146 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

