NO, via its target Cx37, modulates calcium signal propagation selectively at myoendothelial gap junctions
- PMID: 24885166
- PMCID: PMC4036488
- DOI: 10.1186/1478-811X-12-33
NO, via its target Cx37, modulates calcium signal propagation selectively at myoendothelial gap junctions
Abstract
Background: Gap junctional calcium signal propagation (transfer of calcium or a calcium releasing messenger via gap junctions) between vascular cells has been shown to be involved in the control of vascular tone. We have shown before that nitric oxide (NO) inhibits gap junctional communication in HeLa cells exclusively expressing connexin 37 (HeLa-Cx37) but not in HeLa-Cx40 or HeLa-Cx43. Here we studied the effect of NO on the gap junctional calcium signal propagation in endothelial cells which, in addition to Cx37, also express Cx40 and Cx43. Furthermore, we analyzed the impact of NO on intermuscle and on myoendothelial gap junction-dependent calcium signal propagation. Since specific effects of NO at one of these three junctional areas (interendothelial/ myoendothelial/ intermuscle) may depend on a differential membrane localization of the connexins, we also studied the distribution of the vascular connexins in small resistance arteries.
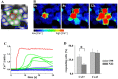
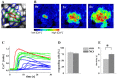
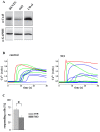
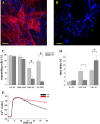
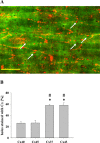
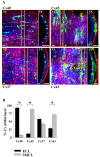
Results: In endothelial (HUVEC) or smooth muscle cells (HUVSMC) alone, NO did not affect gap junctional Ca2+ signal propagation as assessed by analyzing the spread of Ca2+ signals after mechanical stimulation of a single cell. In contrast, at myoendothelial junctions, it decreased Ca2+ signal propagation in both directions by about 60% (co-cultures of HUVEC and HUVSMC). This resulted in a longer maintenance of calcium elevation at the endothelial side and a faster calcium signal propagation at the smooth muscle side, respectively. Immunohistochemical stainings (confocal and two-photon-microscopy) of cells in co-cultures or of small arteries revealed that Cx37 expression was relatively higher in endothelial cells adjoining smooth muscle (culture) or in potential areas of myoendothelial junctions (arteries). Accordingly, Cx37 - in contrast to Cx40 - was not only expressed on the endothelial surface of small arteries but also in deeper layers (corresponding to the internal elastic lamina IEL). Holes of the IEL where myoendothelial contacts can only occur, stained significantly more frequently for Cx37 and Cx43 than for Cx40 (endothelium) or Cx45 (smooth muscle).
Conclusion: NO modulates the calcium signal propagation specifically between endothelial and smooth muscle cells. The effect is due to an augmented distribution of Cx37 towards myoendothelial contact areas and potentially counteracts endothelial Ca2+ signal loss from endothelial to smooth muscle cells. This targeted effect of NO may optimize calcium dependent endothelial vasomotor function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NO Augments Endothelial Reactivity by Reducing Myoendothelial Calcium Signal Spreading: A Novel Role for Cx37 (Connexin 37) and the Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase SHP-2.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Dec;37(12):2280-2290. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309913. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 29025706
-
Heterogeneity in the distribution of vascular gap junctions and connexins: implications for function.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2002 Jul;29(7):620-5. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1681.2002.03699.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12060107
-
Molecular regulation of myoendothelial gap junctions.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2019 Apr;45:16-22. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2019.03.006. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30999095 Review.
-
Decreased intercellular dye-transfer and downregulation of non-ablated connexins in aortic endothelium deficient in connexin37 or connexin40.J Cell Sci. 2003 Jun 1;116(Pt 11):2223-36. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00429. Epub 2003 Apr 15. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12697838
-
Vascular gap junctions and implications for hypertension.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2004 Oct;31(10):659-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2004.04071.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15554905 Review.
Cited by
-
Connexins may play a critical role in cigarette smoke-induced pulmonary hypertension.Arch Toxicol. 2022 Jun;96(6):1609-1621. doi: 10.1007/s00204-022-03274-6. Epub 2022 Mar 27. Arch Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35344070 Review.
-
Gap Junctional Interaction of Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPC) with Endothelial Cells Induces Angiogenic Network Formation In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 18;26(10):4827. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104827. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429968 Free PMC article.
-
Connexins and angiogenesis: Functional aspects, pathogenesis, and emerging therapies (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2022 Aug;50(2):110. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5166. Epub 2022 Jun 28. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35762312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The conducted vasomotor response and the principles of electrical communication in resistance arteries.Physiol Rev. 2024 Jan 1;104(1):33-84. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00035.2022. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Physiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 37410448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of gap junction channels and hemichannels by phosphorylation and redox changes: a revision.BMC Cell Biol. 2016 May 24;17 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12860-016-0099-3. BMC Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27229925 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Severs NJ, Rothery S, Dupont E, Coppen SR, Yeh HI, Ko YS, Matsushita T, Kaba R, Halliday D. Immunocytochemical analysis of connexin expression in the healthy and diseased cardiovascular system. Microsc Res Tech. 2001;52(3):301–322. doi: 10.1002/1097-0029(20010201)52:3<301::AID-JEMT1015>3.0.CO;2-Q. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

