MiR-155 induction in microglial cells suppresses Japanese encephalitis virus replication and negatively modulates innate immune responses
- PMID: 24885259
- PMCID: PMC4050406
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-11-97
MiR-155 induction in microglial cells suppresses Japanese encephalitis virus replication and negatively modulates innate immune responses
Abstract
Background: Microglial cells, which are resident macrophages of the central nervous system, play important roles in immune responses and pathogenesis. Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) is a neurotropic virus that infects microglial cells in brain. Several microRNAs including miR-155 and miR-146a play an important role in defining the microglia inflammatory profile. In this study, we have investigated the effect of miR-155 and miR-146a modulation on JEV infection as well as innate immune responses in human microglial cells.
Methods: In vitro studies were performed in JEV-infected human microglial CHME3 cells. miR-155 or miR-146a were overexpressed and total RNA and protein were extracted following JEV-infection. Expression of genes involved in innate immune responses was studied by PCR array, quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR), western blot and Fluorescence activated cell sorter (FACS). JEV replication was monitored by studying the viral RNA by qPCR, protein by western blot, and titres by plaque assay.
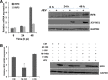
Results: Overexpression of miR-155 in CHME3 cells resulted in significantly reduced JEV replication whereas miR-146a overexpression had an insignificant effect. Additionally, interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8) and complement factor H (CFH) were induced during JEV infection; however, this induction was attenuated in miR-155 overexpressing cells following JEV infection. Further, JEV-induced NF-κB regulated downstream gene expression was attenuated. Interestingly, an increased level of CD45, a negative regulator of microglia activation and a reduced phosphorylated-Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription (p-STAT1) expression was observed in miR-155 overexpressing cells upon JEV infection.
Conclusion: Induction of miR-155 in human microglial cells may negatively modulate JEV-induced innate immune gene expression and may have a beneficial role in limiting JEV replication in human microglial cells.
Figures






Similar articles
-
miR-146a suppresses cellular immune response during Japanese encephalitis virus JaOArS982 strain infection in human microglial cells.J Neuroinflammation. 2015 Feb 18;12:30. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0249-0. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 25889446 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of Interferon (IFN) Regulatory Factor 8 Associated with Restricted IFN-γ Response Augmented Japanese Encephalitis Virus Replication in the Mouse Brain.J Virol. 2021 Oct 13;95(21):e0040621. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00406-21. Epub 2021 Aug 11. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34379515 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory role of TRIM21 in the type-I interferon pathway in Japanese encephalitis virus-infected human microglial cells.J Neuroinflammation. 2014 Feb 1;11:24. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-11-24. J Neuroinflammation. 2014. PMID: 24485101 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of miRNA Regulation in Japanese Encephalitis (JEV) Virus Infection.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024;25(5):521-533. doi: 10.2174/0113892010241606231003102047. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37888811 Review.
-
microRNA-146a-5p, Neurotropic Viral Infection and Prion Disease (PrD).Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 25;22(17):9198. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179198. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502105 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Host Combats IBDV Infection at Both Protein and RNA Levels.Viruses. 2022 Oct 21;14(10):2309. doi: 10.3390/v14102309. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36298864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase 3 can be attenuated by inhibition of microRNA-155 in cultured human astrocytes.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Jul 21;15(1):211. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1245-y. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 30031401 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs of microglia: Wrestling with central nervous system disease.Neural Regen Res. 2018 Dec;13(12):2067-2072. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.241444. Neural Regen Res. 2018. PMID: 30323123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in Neuroinflammation: Implications in Disease Pathogenesis, Biomarker Discovery and Therapeutic Applications.Noncoding RNA. 2019 Apr 24;5(2):35. doi: 10.3390/ncrna5020035. Noncoding RNA. 2019. PMID: 31022830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond HIV infection: Neglected and varied impacts of CCR5 and CCR5Δ32 on viral diseases.Virus Res. 2020 Sep;286:198040. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198040. Epub 2020 May 30. Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 32479976 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

