Performance of seven serological assays for diagnosing tularemia
- PMID: 24885274
- PMCID: PMC4021340
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-234
Performance of seven serological assays for diagnosing tularemia
Abstract
Background: Tularemia is a rare zoonotic disease caused by the Gram-negative bacterium Francisella tularensis. Serology is frequently the preferred diagnostic approach, because the pathogen is highly infectious and difficult to cultivate. The aim of this retrospective study was to determine the diagnostic accuracy of tularemia specific tests.
Methods: The Serazym®Anti-Francisella tularensis ELISA, Serion ELISA classic Francisella tularensis IgG/IgM, an in-house ELISA, the VIRapid® Tularemia immunochromatographic test, an in-house antigen microarray, and a Western Blot (WB) assay were evaluated. The diagnosis tularemia was established using a standard micro-agglutination assay. In total, 135 sera from a series of 110 consecutive tularemia patients were tested.
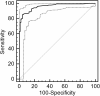
Results: The diagnostic sensitivity and diagnostic specificity of the tests were VIRapid (97.0% and 84.0%), Serion IgG (96.3% and 96.8%), Serion IgM (94.8% and 96.8%), Serazym (97.0% and 91.5%), in-house ELISA (95.6% and 76.6%), WB (93.3% and 83.0%), microarray (91.1% and 97.9%).
Conclusions: The diagnostic value of the commercial assays was proven, because the diagnostic accuracy was >90%. The diagnostic sensitivity of the in-house ELISA and the WB were acceptable, but the diagnostic accuracy was <90%. Interestingly, the antigen microarray test was very specific and had a very good positive predictive value.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Francisella tularensis, Tularemia and Serological Diagnosis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Oct 26;10:512090. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.512090. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33194778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of In-House and Commercial Serological Tests for Diagnosis of Human Tularemia.J Clin Microbiol. 2017 Dec 26;56(1):e01440-17. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01440-17. Print 2018 Jan. J Clin Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29118164 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparison of usefulness of commercial ELISA Virion/Serion, homemade ELISA and tube agglutination test in serodiagnosis of tularemia].Med Dosw Mikrobiol. 2013;65(4):255-61. Med Dosw Mikrobiol. 2013. PMID: 24730213 Polish.
-
A novel screening ELISA and a confirmatory Western blot useful for diagnosis and epidemiological studies of tularemia.Epidemiol Infect. 2005 Aug;133(4):759-66. doi: 10.1017/s0950268805003742. Epidemiol Infect. 2005. PMID: 16050523 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic procedures in tularaemia with special focus on molecular and immunological techniques.J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2005 Aug;52(6):249-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.2005.00863.x. J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2005. PMID: 16219088 Review.
Cited by
-
Usefulness of a single-assay chemiluminescence test (Tularaemia VIRCLIA IgG + IgM monotest) for the diagnosis of human tularemia. Comparison of five serological tests.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018 Apr;37(4):643-649. doi: 10.1007/s10096-017-3155-9. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29280085
-
Epidemiological survey of tularemia in Ilam Province, west of Iran.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Jun 7;19(1):502. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4121-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31174488 Free PMC article.
-
Francisella tularensis, Tularemia and Serological Diagnosis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Oct 26;10:512090. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.512090. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33194778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of In-House and Commercial Serological Tests for Diagnosis of Human Tularemia.J Clin Microbiol. 2017 Dec 26;56(1):e01440-17. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01440-17. Print 2018 Jan. J Clin Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29118164 Free PMC article.
-
Francisella tularensis in Swedish predators and scavengers.Epidemiol Infect. 2019 Oct 22;147:e293. doi: 10.1017/S0950268819001808. Epidemiol Infect. 2019. PMID: 31637994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dennis DT, Inglesby TV, Henderson DA, Bartlett JG, Ascher MS, Eitzen E, Fine AD, Friedlander AM, Hauer J, Layton M, Lillibridge SR, McDade JE, Osterholm MT, O’Toole T, Parker G, Perl TM, Russell PK, Tonat K. Working Group on Civilian Biodefense. Tularemia as a biological weapon: medical and public health management. JAMA. 2001;14(21):2763–2773. doi: 10.1001/jama.285.21.2763. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Splettstoesser W, Guglielmo-Viret V, Seibold E, Thullier P. Evaluation of an immunochromatographic test for rapid and reliable serodiagnosis of human tularemia and detection of Francisella tularensis-specific antibodies in sera from different mammalian species. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;14(5):1629–1634. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01475-09. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

