A comparison of performance of plant miRNA target prediction tools and the characterization of features for genome-wide target prediction
- PMID: 24885295
- PMCID: PMC4035075
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-348
A comparison of performance of plant miRNA target prediction tools and the characterization of features for genome-wide target prediction
Abstract
Background: Deep-sequencing has enabled the identification of large numbers of miRNAs and siRNAs, making the high-throughput target identification a main limiting factor in defining their function. In plants, several tools have been developed to predict targets, majority of them being trained on Arabidopsis datasets. An extensive and systematic evaluation has not been made for their suitability for predicting targets in species other than Arabidopsis. Nor, these have not been evaluated for their suitability for high-throughput target prediction at genome level.
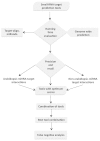
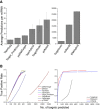
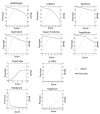
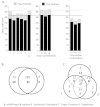
Results: We evaluated the performance of 11 computational tools in identifying genome-wide targets in Arabidopsis and other plants with procedures that optimized score-cutoffs for estimating targets. Targetfinder was most efficient [89% 'precision' (accuracy of prediction), 97% 'recall' (sensitivity)] in predicting 'true-positive' targets in Arabidopsis miRNA-mRNA interactions. In contrast, only 46% of true positive interactions from non-Arabidopsis species were detected, indicating low 'recall' values. Score optimizations increased the 'recall' to only 70% (corresponding 'precision': 65%) for datasets of true miRNA-mRNA interactions in species other than Arabidopsis. Combining the results of Targetfinder and psRNATarget delivers high true positive coverage, whereas the intersection of psRNATarget and Tapirhybrid outputs deliver highly 'precise' predictions. The large number of 'false negative' predictions delivered from non-Arabidopsis datasets by all the available tools indicate the diversity in miRNAs-mRNA interaction features between Arabidopsis and other species. A subset of miRNA-mRNA interactions differed significantly for features in seed regions as well as the total number of matches/mismatches.
Conclusion: Although, many plant miRNA target prediction tools may be optimized to predict targets with high specificity in Arabidopsis, such optimized thresholds may not be suitable for many targets in non-Arabidopsis species. More importantly, non-conventional features of miRNA-mRNA interaction may exist in plants indicating alternate mode of miRNA target recognition. Incorporation of these divergent features would enable next-generation of algorithms to better identify target interactions.
Figures



Similar articles
-
SeqTar: an effective method for identifying microRNA guided cleavage sites from degradome of polyadenylated transcripts in plants.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Feb;40(4):e28. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1092. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22140118 Free PMC article.
-
sPARTA: a parallelized pipeline for integrated analysis of plant miRNA and cleaved mRNA data sets, including new miRNA target-identification software.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Oct;42(18):e139. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku693. Epub 2014 Aug 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25120269 Free PMC article.
-
Protocols for miRNA Target Prediction in Plants.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1970:65-73. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9207-2_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30963488
-
Finding microRNA targets in plants: current status and perspectives.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2012 Oct;10(5):264-75. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2012.09.003. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 23200136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Popular Computational Tools Used for miRNA Prediction and Their Future Development Prospects.Interdiscip Sci. 2020 Dec;12(4):395-413. doi: 10.1007/s12539-020-00387-3. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Interdiscip Sci. 2020. PMID: 32959233 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA Zma-miR528 Versatile Regulation on Target mRNAs during Maize Somatic Embryogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 18;22(10):5310. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105310. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34069987 Free PMC article.
-
Computational screening of miRNAs and their targets in saffron (Crocus sativus L.) by transcriptome mining.Planta. 2021 Nov 9;254(6):117. doi: 10.1007/s00425-021-03761-7. Planta. 2021. PMID: 34751821
-
A novel computational approach to the silencing of Sugarcane Bacilliform Guadeloupe A Virus determines potential host-derived MicroRNAs in sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.).PeerJ. 2020 Jan 13;8:e8359. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8359. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 31976180 Free PMC article.
-
The green peach aphid gut contains host plant microRNAs identified by comprehensive annotation of Brassica oleracea small RNA data.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 11;9(1):18904. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54488-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31827121 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs target databases: developmental methods and target identification techniques with functional annotations.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Jun;74(12):2239-2261. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2469-1. Epub 2017 Feb 15. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28204845 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pandey SP, Moturu TR, Pandey P. Roles of Small RNAs in Regulation of Signaling and Adaptive Responses in Plants. In: Mandal SS, editor. Recent Trends in Gene Expression. Hauppauge, NY: Nova Publishers; 2013. pp. 107–132.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

