Comparing the functional impact of knee replacements in two cohorts
- PMID: 24885404
- PMCID: PMC4016673
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-15-145
Comparing the functional impact of knee replacements in two cohorts
Abstract
Background: To examine if different rates of total knee replacement (TKR) in two similar cohorts with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis (OA) were associated with different functional impact of disease.
Methods: Subjects from the Multicenter Osteoarthritis Study (MOST) and the Osteoarthritis Initiative (OAI), persons with or at high risk of OA, had knee radiographs, completed Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) surveys and had TKRs confirmed at each visit. At each visit, subjects were defined as having symptomatic OA (SxOA) if ≥ one knee had pain and radiographic OA or if they had a TKR. WOMAC function scores at each visit were compared by analysis of covariance adjusting for age, sex, body mass index, race, site, depression, comorbidity, painful leg joints and knees affected. Post-TKR function scores were imputed to estimate scores that would have been present without TKR.
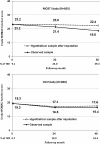
Results: Subjects with SxOA (n>750 in MOST and in OAI) had a mean age 66 to 67 years; most were women and were White. Subjects were followed 4-5 years. Among those with SxOA, more TKRs were done in MOST (35%) than OAI (19%). Adjusted mean WOMAC function (0-68, 68 = worst) improved from 26.9 to 21.9 in MOST and from 24.5 to 22.0 in OAI (difference between MOST and OAI in change in WOMAC function, p = .01). Estimates of function without TKRs showed function would not have changed in MOST (23.2 at baseline to 22.4).
Conclusions: Functional status of subjects with knee OA in MOST improved more than in OAI, probably because of higher rates of TKRs. The decline suggests that TKR diminishes the functional impact of OA in the community.
Figures
References
-
- Lawrence RC, Felson DT, Helmick CG, Arnold LM, Choi H, Deyo RA, Gabriel S, Hirsch R, Hochberg MC, Hunder GG, Jordan JM, Katz JN, Kremers HM, Wolfe F. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. Part II. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(1):26–35. doi: 10.1002/art.23176. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, national Center for Health Statistics. QuickStats: rate of total knee replacement for persons aged ≥65 years, by sex - United States, 1979–2002. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2005;54:179.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical