The challenge to avoid anti-malarial medicine stock-outs in an era of funding partners: the case of Tanzania
- PMID: 24885420
- PMCID: PMC4030285
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-181
The challenge to avoid anti-malarial medicine stock-outs in an era of funding partners: the case of Tanzania
Abstract
Background: Between 2007 and 2013, the Tanzanian public sector received 93.1 million doses of first-line anti-malarial artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) in the form of artemether-lumefantrine entirely supplied by funding partners. The introduction of a health facility ACT stock monitoring system using SMS technology by the National Malaria Control Programme in mid 2011 revealed a high frequency of stock-outs of ACT in primary care public health facilities. The objective of this study was to determine the pattern of availability of ACT and possible causes of observed stock-outs across public health facilities in Tanzania since mid-2011.
Methods: Data were collected weekly by the mobile phone reporting tool SMS for Life on ACT availability from over 5,000 public health facilities in Tanzania starting from September 2011 to December 2012. Stock data for all four age-dose levels of ACT across health facilities were summarized and supply of ACT at the national level was also documented.
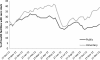
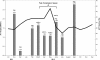
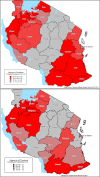
Results: Over the period of 15 months, on average 29% of health facilities in Tanzania were completely stocked out of all four-age dose levels of the first-line anti-malarial with a median duration of total stock-out of six weeks. Patterns of total stock-out by region ranged from a low of 9% to a high of 52%. The ACT stock-outs were most likely caused by: a) insufficient ACT supplies entering Tanzania (e.g. in 2012 Tanzania received 10.9 million ACT doses compared with a forecast demand of 14.4 million doses); and b) irregular pattern of ACT supply (several months with no ACT stock).
Conclusion: The reduced ACT availability and irregular pattern of supply were due to cumbersome bureaucratic processes and delays both within the country and from the main donor, the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria. Tanzania should invest in strengthening both the supply system and the health information system using mHealth solutions such as SMS for Life. This will continue to assist in tracking ACT availability across the country where all partners work towards more streamlined, demand driven and accountable procurement and supply chain systems.
Figures

References
-
- National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), Office of the Chief Government Statistician (OCGS), CF International. Tanzania HIV/AIDS and Malaria Indicator Survey 2011–2012. Dar es Salaam, Tanzania: TACAIDS, ZAC, NBS, OCGS, ICF International; 2013.
-
- National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), Chief Government Statistician (OCGS), Macro International Inc. Tanzania HIV/AIDS and Malaria Indicator Survey 2007–2008. Dar es Salaam, Tanzania: TACAIDS, ZAC, NBS, OCGS, and Macro International Inc; 2009.
-
- Ministry of Health and Social Welfare Tanzania. Tanzania Mainland National Health Accounts 2009/10. Dar es Salaam, Tanzania: Ministry of Health and Social Welfare Tanzania; 2010.
-
- The Global Fund to Fight AIDS Tuberculosis and Malaria. Proposal Form - Round 9 Tanzania. Geneva: GFATM; 2009. - PubMed
-
- Ministry of Health and Social Welfare Tanzania. Health sector performance profile report, Mainland Tanzania July 2006 - June 2007. Dar es Salaam, Tanzania: Ministry of Health and Social Welfare Tanzania; 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

