Minireview: transgenerational epigenetic inheritance: focus on endocrine disrupting compounds
- PMID: 24885575
- PMCID: PMC4098001
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2014-1123
Minireview: transgenerational epigenetic inheritance: focus on endocrine disrupting compounds
Abstract
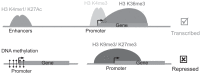
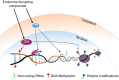
The idea that what we eat, feel, and experience influences our physical and mental state and can be transmitted to our offspring and even to subsequent generations has been in the popular realm for a long time. In addition to classic gene mutations, we now recognize that some mechanisms for inheritance do not require changes in DNA. The field of epigenetics has provided a new appreciation for the variety of ways biological traits can be transmitted to subsequent generations. Thus, transgenerational epigenetic inheritance has emerged as a new area of research. We have four goals for this minireview. First, we describe the topic and some of the nomenclature used in the literature. Second, we explain the major epigenetic mechanisms implicated in transgenerational inheritance. Next, we examine some of the best examples of transgenerational epigenetic inheritance, with an emphasis on those produced by exposing the parental generation to endocrine-disrupting compounds (EDCs). Finally, we discuss how whole-genome profiling approaches can be used to identify aberrant epigenomic features and gain insight into the mechanism of EDC-mediated transgenerational epigenetic inheritance. Our goal is to educate readers about the range of possible epigenetic mechanisms that exist and encourage researchers to think broadly and apply multiple genomic and epigenomic technologies to their work.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

