Lactate dehydrogenase A is a potential prognostic marker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 24885701
- PMCID: PMC4022787
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-101
Lactate dehydrogenase A is a potential prognostic marker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Over 90% of cancer-related deaths in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC) are caused by tumor relapse and metastasis. Thus, there is an urgent need for new molecular markers that can potentiate the efficacy of the current clinical-based models of prognosis assessment. The objective of this study is to evaluate the potential significance of lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA), assessed by immunohistochemical staining, as a prognostic marker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma in relation to clinicopathological features and clinical outcome.
Methods: We assessed the expression of LDHA at the protein level, by immunohistochemistry, and correlated its expression with multiple clinicopathological features including tumor size, clinical stage, histological grade, disease-free and overall survival in 385 patients with primary clear cell renal cell carcinoma. We also correlated the LDHA expression with overall survival, at mRNA level, in an independent data set of 170 clear cell renal cell carcinoma cases from The Cancer Genome Atlas databases. Cox proportional hazards models adjusted for the potential clinicopathological factors were used to test for associations between the LDHA expression and both disease-free survival and overall survival.
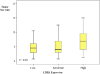
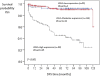
Results: There is statistically significant positive correlation between LDHA level of expression and tumor size, clinical stage and histological grade. Moreover, LDHA expression shows significantly inverse correlation with both disease-free survival and overall survival in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Our results are validated by examining LDHA expression, at the mRNA level, in the independent data set of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cases from The Cancer Genome Atlas databases which also shows that higher lactate dehydrogenase A expression is associated with significantly shorter overall survival.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that LDHA up-regulation can be a predictor of poor prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Thus, it represents a potential prognostic biomarker that can boost the accuracy of other prognostic models in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
Figures



References
-
- Heng DY, Xie W, Regan MM, Harshman LC, Bjarnason GA, Vaishampayan UN, Mackenzie M, Wood L, Donsko F, Tan MH, Rha SY, Agarwal N, Kollmannsberger C, Rini BI, Choueiri TK. External validation and comparison with other models of the International Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium prognostic model: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:141–148. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70559-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Heng DY, Xie W, Regan MM, Warren MA, Golshayan AR, Sahi C, Eigl BJ, Ruether JD, Cheng T, North S, Venner P, Knox JJ, Chi KN, Kollmannsberger C, McDermott DF, Oh WK, Atkins MB, Bukowski RM, Rini BI, Choueiri TK. Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted agents: results from a large, multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:5794–5799. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.21.4809. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

