Asbestos modulates thioredoxin-thioredoxin interacting protein interaction to regulate inflammasome activation
- PMID: 24885895
- PMCID: PMC4055279
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-8977-11-24
Asbestos modulates thioredoxin-thioredoxin interacting protein interaction to regulate inflammasome activation
Abstract
Background: Asbestos exposure is related to various diseases including asbestosis and malignant mesothelioma (MM). Among the pathogenic mechanisms proposed by which asbestos can cause diseases involving epithelial and mesothelial cells, the most widely accepted one is the generation of reactive oxygen species and/or depletion of antioxidants like glutathione. It has also been demonstrated that asbestos can induce inflammation, perhaps due to activation of inflammasomes.
Methods: The oxidation state of thioredoxin was analyzed by redox Western blot analysis and ROS generation was assessed spectrophotometrically as a read-out of solubilized formazan produced by the reduction of nitrotetrazolium blue (NTB) by superoxide. Quantitative real time PCR was used to assess changes in gene transcription.
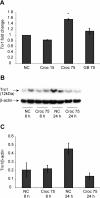
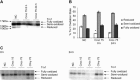
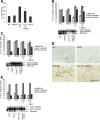
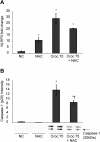
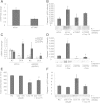
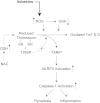
Results: Here we demonstrate that crocidolite asbestos fibers oxidize the pool of the antioxidant, Thioredoxin-1 (Trx1), which results in release of Thioredoxin Interacting Protein (TXNIP) and subsequent activation of inflammasomes in human mesothelial cells. Exposure to crocidolite asbestos resulted in the depletion of reduced Trx1 in human peritoneal mesothelial (LP9/hTERT) cells. Pretreatment with the antioxidant dehydroascorbic acid (a reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenger) reduced the level of crocidolite asbestos-induced Trx1 oxidation as well as the depletion of reduced Trx1. Increasing Trx1 expression levels using a Trx1 over-expression vector, reduced the extent of Trx1 oxidation and generation of ROS by crocidolite asbestos, and increased cell survival. In addition, knockdown of TXNIP expression by siRNA attenuated crocidolite asbestos-induced activation of the inflammasome.
Conclusion: Our novel findings suggest that extensive Trx1 oxidation and TXNIP dissociation may be one of the mechanisms by which crocidolite asbestos activates the inflammasome and helps in development of MM.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of high glucose-based peritoneal dialysis fluids on thioredoxin-interacting protein expression in human peritoneal mesothelial cells.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Jan;66:198-204. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.11.027. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30471618
-
Thioredoxin-interacting protein mediates TRX1 translocation to the plasma membrane in response to tumor necrosis factor-α: a key mechanism for vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 transactivation by reactive oxygen species.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011 Aug;31(8):1890-7. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.226340. Epub 2011 Jun 2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011. PMID: 21636804
-
Antioxidants prevent the RhoA inhibition evoked by crocidolite asbestos in human mesothelial and mesothelioma cells.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011 Sep;45(3):625-31. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0089OC. Epub 2011 Jan 21. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21257924
-
Thioredoxin promotes survival signaling events under nitrosative/oxidative stress associated with cancer development.Biomed J. 2017 Aug;40(4):189-199. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Jul 29. Biomed J. 2017. PMID: 28918907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asbestos-induced mesothelial injury and carcinogenesis: Involvement of iron and reactive oxygen species.Pathol Int. 2022 Feb;72(2):83-95. doi: 10.1111/pin.13196. Epub 2021 Dec 29. Pathol Int. 2022. PMID: 34965001 Review.
Cited by
-
Innate Immunity and Biomaterials at the Nexus: Friends or Foes.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:342304. doi: 10.1155/2015/342304. Epub 2015 Jul 12. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26247017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TXNIP regulates pulmonary inflammation induced by Asian sand dust.Redox Biol. 2024 Dec;78:103421. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103421. Epub 2024 Nov 6. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 39520910 Free PMC article.
-
Asbestos-induced chronic inflammation in malignant pleural mesothelioma and related therapeutic approaches-a narrative review.Precis Cancer Med. 2021 Sep;4:27. doi: 10.21037/pcm-21-12. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Precis Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 35098108 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of autoantibody profiles in two asbestiform fiber exposure cohorts.J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2018;81(19):1015-1027. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2018.1512432. Epub 2018 Sep 19. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2018. PMID: 30230971 Free PMC article.
-
Cigarette smoke represses the innate immune response to asbestos.Physiol Rep. 2015 Dec;3(12):e12652. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12652. Physiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26660560 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

