Survival advantage of partial over radical nephrectomy in patients presenting with localized renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 24885955
- PMCID: PMC4038042
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-372
Survival advantage of partial over radical nephrectomy in patients presenting with localized renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Partial nephrectomy (PN) preserves renal function and has become the standard approach for T1a renal cell carcinoma (RCC). However, there is still an ongoing debate as to which patients will actually derive greater benefit from partial than from radical nephrectomy (RN). The aim of this study was to retrospectively evaluate the impact of the type of surgery on overall survival (OS) in patients with localized RCC.
Methods: Renal surgery was performed in 4326 patients with localized RCC (pT ≤ 3a N/M0) at six German tertiary care centers from 1980 to 2010: RN in 2955 cases (68.3%), elective (ePN) in 1108 (25.6%), and imperative partial nephrectomy (iPN) in 263 (6.1%) cases. The median follow-up for all patients was 63 months. Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression analyses were carried out to identify prognosticators for OS.
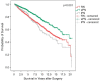
Results: PN was performed significantly more often than RN in patients presenting with lower tumor stages, higher RCC differentiation, and non-clear cell histology. Accordingly, the calculated 5 (10)-year OS rates were 90.0 (74.6)% for ePN, 83.9 (57.5)% for iPN, and 81.2 (64.7)% for RN (p < 0.001). However, multivariate analysis including age, sex, tumor diameter and differentiation, histological subtype, and the year of surgery showed that ePN compared to RN still qualified as an independent factor for improved OS (HR 0.79, 95% CI 0.66-0.94, p = 0.008).
Conclusion: Even allowing for the weaknesses of this retrospective analysis, our multicenter study indicates that in patients with localized RCC, PN appears to be associated with better OS than RN irrespective of age or tumor size.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Partial nephrectomy is not associated with an overall survival advantage over radical nephrectomy in elderly patients with stage Ib-II renal masses: An analysis of the national cancer data base.Cancer. 2018 Oct 1;124(19):3839-3848. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31582. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30207380
-
Survival after partial and radical nephrectomy for the treatment of stage T1bN0M0 renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in the USA: a propensity scoring approach.BJU Int. 2012 May;109(10):1457-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10597.x. Epub 2011 Sep 20. BJU Int. 2012. PMID: 21933334
-
Comparison of prognosis between patients undergoing radical nephrectomy versus partial nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma ≤7 cm T3aN0/xM0: Survival benefit is biased toward partial nephrectomy.Cancer Med. 2021 Dec;10(24):8909-8923. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4412. Epub 2021 Nov 14. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34779154 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the long-term follow-up and perioperative outcomes of partial nephrectomy and radical nephrectomy for 4 cm to 7 cm renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Urol. 2019 Jun 7;19(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12894-019-0480-6. BMC Urol. 2019. PMID: 31174522 Free PMC article.
-
The expanding role of partial nephrectomy: a critical analysis of indications, results, and complications.Eur Urol. 2010 Feb;57(2):214-22. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.10.019. Epub 2009 Oct 20. Eur Urol. 2010. PMID: 19853988 Review.
Cited by
-
Objective assessment of intraoperative skills for robot-assisted partial nephrectomy (RAPN).J Robot Surg. 2023 Aug;17(4):1401-1409. doi: 10.1007/s11701-023-01521-1. Epub 2023 Jan 23. J Robot Surg. 2023. PMID: 36689078 Free PMC article.
-
Outcome of laparoscopic nephron sparing surgery using a Satinsky clamp for hilar control: a trusted tool (SKIMS experience).Curr Urol. 2021 Sep;15(3):172-175. doi: 10.1097/CU9.0000000000000022. Epub 2021 May 20. Curr Urol. 2021. PMID: 34552458 Free PMC article.
-
Partial nephrectomy for T3aN0M0 renal cell carcinoma: shall we step forward?Int Braz J Urol. 2017 Sep-Oct;43(5):849-856. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0598. Int Braz J Urol. 2017. PMID: 28792193 Free PMC article.
-
Oncological and functional efficacy of nephron-sparing surgery versus radical nephrectomy in renal cell carcinoma stages ≥cT1b: a single institution, matched analysis.Cent European J Urol. 2018;71(1):48-57. doi: 10.5173/ceju.2017.1611. Epub 2017 Dec 22. Cent European J Urol. 2018. PMID: 29732207 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of oncologic and functional outcomes in patients with pt3a renal cell carcinoma treated with partial and radical nephrectomy.Int Braz J Urol. 2021 Jul-Aug;47(4):777-783. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2020.0149. Int Braz J Urol. 2021. PMID: 33848068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sun M, Abdollah F, Bianchi M, Trinh QD, Jeldres C, Thuret R, Tian Z, Shariat SF, Montorsi F, Perrotte P, Karakiewicz PI. Treatment management of small renal masses in the 21st century: a paradigm shift. Annals of surgical oncology. 2012;19(7):2380–2387. doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2247-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Antonelli A, Ficarra V, Bertini R, Carini M, Carmignani G, Corti S, Longo N, Martorana G, Minervini A, Mirone V, Novara G, Serni S, Simeone C, Simonato A, Siracusano S, Volpe A, Zattoni F, Cunico SC. Elective partial nephrectomy is equivalent to radical nephrectomy in patients with clinical T1 renal cell carcinoma: results of a retrospective, comparative, multi-institutional study. BJU Int. 2012;109(7):1013–1018. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10431.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

