Modulation of insulin/IGFs pathways by sirtuin-7 inhibition in drug-induced chemoreistance
- PMID: 24885964
- PMCID: PMC4229859
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-1596-9-94
Modulation of insulin/IGFs pathways by sirtuin-7 inhibition in drug-induced chemoreistance
Abstract
Background: Insulin and insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) are key regulators of metabolism and growth. Recent evidences suggest a key role of these pathways in non-classical tissues and the metabolic pathways by which these hormones exert their effects in neoplasia is unclear.
Aims: To study insulin/IGFs pathways in drug sensitive and resistant cancer cells representing breast cancer (MCF-7), osteosarcoma (SaOS-2), and ovarian cancer (A2780) and to examine the effect of Sirtuin-7 (Sirt7) inhibition on insulin/IGFs pathways in MCF-7 cell line.
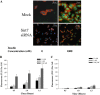
Methods: Drug resistant cells were generated by continuous incubation of parental cell lines with stepwise increases in Doxorubicin or Cisplatin over a period of 3 to 6 months. MCF-7 cells were transfected with cloned hairpin siRNA template for Sirt7 using the Amaxa GmbH transfection system. mRNA expression of Sirt7, INSR, IRS-1, IRS-2, IRS-4, IGF-1, IGF-2, MDR-1, MRP-1, BCRP was measured by qPCR and Sirt7 by standard Western blotting. FITC-insulin uptake was imaged with Leica Confocal Microscope.
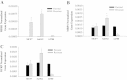
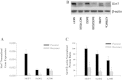
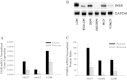
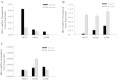
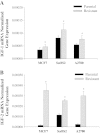
Results: Insulin receptor (INSR), insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) were inhibited in drug-induced resistance, whereas IRS-2 was significantly induced in all the chemoresistant cells tested when compared to their parental counterparts. IGF-1 and IGF-2 were also upregulated in all the drug resistant cells tested. Sirt7 was significantly reduced in all chemoresistant cells tested. Knockdown of Sirt7 expression in human breast MCF-7 cell line by siRNA induced premature senescence-like phenotype and multi-drug resistance, suggesting that this gene may play an active role in regulating cancer cell response to stress. Suppression of Sirt7 selectively inhibited INSR and IRS-1, whereas it had minimal effect on that of IRS-2. Sirt7 suppression in MCF-7 also inhibited insulin uptake. Additionally, Sirt7 inhibition upregulated IGF-1, IGF-2 and IGFR expression.
Conclusion: Our data demonstrate that stress-induced Sirt7 inhibition significantly increases stress resistance and modulates insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathways. More importantly, this study links Sir2 family proteins to insulin/IGF signaling in drug-induced stress resistance in neoplasia.
Virtual slides: The virtual slide(s) for this article can be found here: http://www.diagnosticpathology.diagnomx.eu/vs/1135426681234493.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Insulin receptor substrate-1 involvement in epidermal growth factor receptor and insulin-like growth factor receptor signalling: implication for Gefitinib ('Iressa') response and resistance.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008 Sep;111(1):79-91. doi: 10.1007/s10549-007-9763-9. Epub 2007 Sep 28. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008. PMID: 17902048
-
Progesterone crosstalks with insulin-like growth factor signaling in breast cancer cells via induction of insulin receptor substrate-2.Oncogene. 2003 Oct 9;22(44):6937-41. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206803. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 14534541
-
Role of the insulin-like growth factor system on an estrogen-dependent cancer phenotype in the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2008 Mar;109(1-2):185-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.10.006. Epub 2008 Feb 8. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18337089
-
Insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling in tumorigenesis and drug resistance: a challenge for cancer therapy.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Jun 3;13(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00904-3. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32493414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions between estrogen and insulin-like growth factor signaling pathways in human breast tumor cells.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2003 Jun;10(2):331-45. doi: 10.1677/erc.0.0100331. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12790794 Review.
Cited by
-
Evodiamine inhibits growth of vemurafenib drug-resistant melanoma via suppressing IRS4/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.J Nat Med. 2024 Mar;78(2):342-354. doi: 10.1007/s11418-023-01769-9. Epub 2024 Feb 7. J Nat Med. 2024. PMID: 38324123
-
Does insulin make breast cancer cells resistant to doxorubicin toxicity?Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Nov;396(11):3111-3122. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02516-3. Epub 2023 May 25. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37231169
-
Acute Treatment of Resveratrol Alleviates Doxorubicin-Induced Myotoxicity in Aged Skeletal Muscle Through SIRT1-Dependent Mechanisms.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2016 Jun;71(6):730-9. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glv175. Epub 2015 Oct 8. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 26450947 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Sirtuins in Chronic Degenerative Diseases: New Metabolic Targets in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 16;23(6):3212. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063212. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT7: the seventh key to unlocking the mystery of aging.Physiol Rev. 2024 Jan 1;104(1):253-280. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00044.2022. Epub 2023 Sep 7. Physiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 37676263 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cullen KJ, Yee D, Sly WS, Perdue J, Hampton B, Lippman ME, Rosen N. Insulin-like growth factor receptor expression and function in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1990;50:48–53. - PubMed
-
- Gross GE, Boldt DH, Osborne CK. Perturbation by insulin of human breast cancer cell cycle kinetics. Cancer Res. 1984;44:3570–3575. - PubMed
-
- Myal Y, Shiu RP, Bhaumick B, Bala M. Receptor binding and growth-promoting activity of insulin-like growth factors in human breast cancer cells (T-47D) in culture. Cancer Res. 1984;44:5486–5490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

