In vitro study of the replication capacity of the RGNNV and the SJNNV betanodavirus genotypes and their natural reassortants in response to temperature
- PMID: 24885997
- PMCID: PMC4050099
- DOI: 10.1186/1297-9716-45-56
In vitro study of the replication capacity of the RGNNV and the SJNNV betanodavirus genotypes and their natural reassortants in response to temperature
Abstract
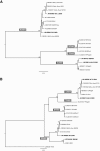
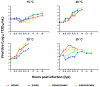
Betanodaviruses are the causative agents of viral nervous necrosis and affect a broad range of fish species worldwide. Their bi-segmented genome is composed of the RNA1 and the RNA2 molecules encoding the viral polymerase and the coat protein, respectively. In southern Europe the presence of the RGNNV and the SJNNV genotypes, and the RGNNV/SJNNV and RGNNV/SJNNV reassortants has been documented. Several studies have reported a correlation between water temperature and disease onset. To explore the replication efficiency of betanodaviruses with different genomes in relation to temperature and to understand the role of genetic reassortment on viral phenotype, RGNNV, SJNNV, RGNNV/SJNNV and RGNNV/SJNNV field isolates were fully sequenced, and growth curves generated in vitro at four different temperatures (15, 20, 25, 30 °C) were developed for each isolate. The data obtained, corroborated by statistical analysis, demonstrated that viral titres of diverse betanodavirus genotypes varied significantly in relation to the incubation temperature of the culture. In particular, at 30 °C betanodaviruses under investigation presented different phenotypes, and viruses containing the RNA1 of the RGNNV genotype showed the best replication efficiency. Laboratory results demonstrated that viruses clustering within the same genotype based on the polymerase gene, possess similar growth kinetics in response to temperature, thus highlighting the key role of RNA1 in controlling viral replication at different environmental conditions. The results generated might have practical implications for the inference of viral phenotype according to genetic features and may contribute to a better understanding of betanodavirus ecology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Water temperature affects pathogenicity of different betanodavirus genotypes in experimentally challenged Dicentrarchus labrax.Dis Aquat Organ. 2016 May 26;119(3):231-8. doi: 10.3354/dao03003. Dis Aquat Organ. 2016. PMID: 27225206
-
Amino acidic substitutions in the polymerase N-terminal region of a reassortant betanodavirus strain causing poor adaptation to temperature increase.Vet Res. 2019 Jun 21;50(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13567-019-0669-4. Vet Res. 2019. PMID: 31227007 Free PMC article.
-
Betanodavirus infection in bath-challenged Solea senegalensis juveniles: A comparative analysis of RGNNV, SJNNV and reassortant strains.J Fish Dis. 2018 Oct;41(10):1571-1578. doi: 10.1111/jfd.12865. Epub 2018 Jul 20. J Fish Dis. 2018. PMID: 30028012
-
Experimental susceptibility of European sea bass and Senegalese sole to different betanodavirus isolates.Vet Microbiol. 2015 May 15;177(1-2):53-61. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.02.030. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Vet Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25770892
-
Understanding the interaction between Betanodavirus and its host for the development of prophylactic measures for viral encephalopathy and retinopathy.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016 Jun;53:35-49. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2016.03.033. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26997200 Review.
Cited by
-
Towards a Dual Lateral Flow Nanobiosensor for Simultaneous Detection of Virus Genotype-Specific PCR Products.J Anal Methods Chem. 2018 Feb 20;2018:7691014. doi: 10.1155/2018/7691014. eCollection 2018. J Anal Methods Chem. 2018. PMID: 29675287 Free PMC article.
-
Betanodavirus and VER Disease: A 30-year Research Review.Pathogens. 2020 Feb 9;9(2):106. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9020106. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32050492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The genetic variability and evolution of red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus quasispecies can be associated with its virulence.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jun 15;14:1182695. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1182695. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37396376 Free PMC article.
-
Viral nervous necrosis in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) caused by reassortant betanodavirus RGNNV/SJNNV: an emerging threat for Mediterranean aquaculture.Sci Rep. 2017 May 2;7:46755. doi: 10.1038/srep46755. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28462930 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors associated with viral nervous necrosis in hybrid groupers in Malaysia and the high similarity of its causative agent nervous necrosis virus to reassortant red-spotted grouper nervous necrosis virus/striped jack nervous necrosis virus strains.Vet World. 2019 Aug;12(8):1273-1284. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2019.1273-1284. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Vet World. 2019. PMID: 31641308 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

