RNA-seq based SNPs for mapping in Brassica juncea (AABB): synteny analysis between the two constituent genomes A (from B. rapa) and B (from B. nigra) shows highly divergent gene block arrangement and unique block fragmentation patterns
- PMID: 24886001
- PMCID: PMC4045973
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-396
RNA-seq based SNPs for mapping in Brassica juncea (AABB): synteny analysis between the two constituent genomes A (from B. rapa) and B (from B. nigra) shows highly divergent gene block arrangement and unique block fragmentation patterns
Abstract
Background: Brassica juncea (AABB) is an allotetraploid species containing genomes of B. rapa (AA) and B. nigra (BB). It is a major oilseed crop in South Asia, and grown on approximately 6-7 million hectares of land in India during the winter season under dryland conditions. B. juncea has two well defined gene pools--Indian and east European. Hybrids between the two gene pools are heterotic for yield. A large number of qualitative and quantitative traits need to be introgressed from one gene pool into the other. This study explores the availability of SNPs in RNA-seq generated contigs, and their use for general mapping, fine mapping of selected regions, and comparative arrangement of gene blocks on B. juncea A and B genomes.
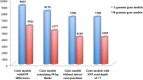
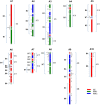
Results: RNA isolated from two lines of B. juncea--Varuna (Indian type) and Heera (east European type)--was sequenced using Illumina paired end sequencing technology, and assembled using the Velvet de novo programme. A and B genome specific contigs were identified in two steps. First, by aligning contigs against the B. rapa protein database (available at BRAD), and second by comparing percentage identity at the nucleotide level with B. rapa CDS and B. nigra transcriptome. 135,693 SNPs were recorded in the assembled partial gene models of Varuna and Heera, 85,473 in the A genome and 50,236 in the B. Using KASpar technology, 999 markers were added to an earlier intron polymorphism marker based map of a B. juncea Varuna x Heera DH population. Many new gene blocks were identified in the B genome. A number of SNP markers covered single copy homoeologues of the A and B genomes, and these were used to identify homoeologous blocks between the two genomes. Comparison of the block architecture of A and B genomes revealed extensive differences in gene block associations and block fragmentation patterns.
Conclusions: Sufficient SNP markers are available for general and specific -region fine mapping of crosses between lines of two diverse B. juncea gene pools. Comparative gene block arrangement and block fragmentation patterns between A and B genomes support the hypothesis that the two genomes evolved from independent hexaploidy events.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A chromosome-scale assembly of allotetraploid Brassica juncea (AABB) elucidates comparative architecture of the A and B genomes.Plant Biotechnol J. 2021 Mar;19(3):602-614. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13492. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Plant Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 33073461 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-seq based SNPs in some agronomically important oleiferous lines of Brassica rapa and their use for genome-wide linkage mapping and specific-region fine mapping.BMC Genomics. 2013 Jul 9;14:463. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-463. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23837684 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative mapping of Brassica juncea and Arabidopsis thaliana using Intron Polymorphism (IP) markers: homoeologous relationships, diversification and evolution of the A, B and C Brassica genomes.BMC Genomics. 2008 Mar 3;9:113. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-113. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18315867 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping of yield influencing QTL in Brassica juncea: implications for breeding of a major oilseed crop of dryland areas.Theor Appl Genet. 2007 Oct;115(6):807-17. doi: 10.1007/s00122-007-0610-5. Epub 2007 Jul 24. Theor Appl Genet. 2007. PMID: 17646960
-
Insights on SNP types, detection methods and their utilization in Brassica species: Recent progress and future perspectives.J Biotechnol. 2020 Dec 20;324:11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2020.09.018. Epub 2020 Sep 24. J Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32979432 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Evolution of Receptor-Like Kinases (RLKs) and Receptor like Proteins (RLPs) in Brassica juncea.Biology (Basel). 2020 Dec 30;10(1):17. doi: 10.3390/biology10010017. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33396674 Free PMC article.
-
A highly contiguous genome assembly of Brassica nigra (BB) and revised nomenclature for the pseudochromosomes.BMC Genomics. 2020 Dec 11;21(1):887. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07271-w. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33308149 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering allelic variations for seed glucosinolate traits in oilseed mustard (Brassica juncea) using two bi-parental mapping populations.Theor Appl Genet. 2015 Apr;128(4):657-66. doi: 10.1007/s00122-015-2461-9. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Theor Appl Genet. 2015. PMID: 25628164
-
A chromosome-scale assembly of allotetraploid Brassica juncea (AABB) elucidates comparative architecture of the A and B genomes.Plant Biotechnol J. 2021 Mar;19(3):602-614. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13492. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Plant Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 33073461 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification, Expression, and Protein Analysis of CKX and IPT Gene Families in Radish (Raphanus sativus L.) Reveal Their Involvement in Clubroot Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 17;25(16):8974. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168974. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UN Genome analysis of Brassica with special reference to the experimental formation of B. napus and peculiar mode of fertilization. Japan J Bot. 1935;7:389–452.
-
- Edward D, Batley J, Parkin IA, Kole C. Genetics, Genomics and Breeding of Oilseed Brassicas. Boca Raton, FL, USA: CRC Press; 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

