Fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with skull base metastases from systemic cancer involving the anterior visual pathway
- PMID: 24886280
- PMCID: PMC4036429
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-9-110
Fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with skull base metastases from systemic cancer involving the anterior visual pathway
Abstract
Background: To analyze the tumor control, survival outcomes, and toxicity after stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for skull base metastases from systemic cancer involving the anterior visual pathway.
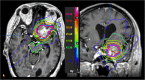
Patients and methods: We have analyzed 34 patients (23 females and 11 males, median age 59 years) who underwent multi-fraction SRS for a skull base metastasis compressing or in close proximity of optic nerves and chiasm. All metastases were treated with frameless LINAC-based multi-fraction SRS in 5 daily fractions of 5 Gy each. Local control, distant failure, and overall survival were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method calculated from the time of SRS. Prognostic variables were assessed using log-rank and Cox regression analyses.
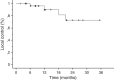
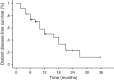
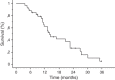
Results: At a median follow-up of 13 months (range, 2-36.5 months), twenty-five patients had died and 9 were alive. The 1-year and 2-year local control rates were 89% and 72%, and respective actuarial survival rates were 63% and 30%. Four patients recurred with a median time to progression of 12 months (range, 6-27 months), and 17 patients had new brain metastases at distant brain sites. The 1-year and 2-year distant failure rates were 50% and 77%, respectively. On multivariate analysis, a Karnofsky performance status (KPS) >70 and the absence of extracranial metastases were prognostic factors associated with lower distant failure rates and longer survival. After multi-fraction SRS, 15 (51%) out of 29 patients had a clinical improvement of their preexisting cranial deficits. No patients developed radiation-induced optic neuropathy during the follow-up.
Conclusions: Multi-fraction SRS (5 x 5 Gy) is a safe treatment option associated with good local control and improved cranial nerve symptoms for patients with a skull base metastasis involving the anterior visual pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Single- and Multi-Fraction Stereotactic Radiosurgery Dose Tolerances of the Optic Pathways.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 May 1;110(1):87-99. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.01.053. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 29534899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skull base chondrosarcoma radiosurgery: report of the North American Gamma Knife Consortium.J Neurosurg. 2015 Nov;123(5):1268-75. doi: 10.3171/2014.12.JNS132580. Epub 2015 Jun 26. J Neurosurg. 2015. PMID: 26115468
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery for intracranial hemangiopericytomas: a multicenter study.J Neurosurg. 2017 Mar;126(3):744-754. doi: 10.3171/2016.1.JNS152860. Epub 2016 Apr 22. J Neurosurg. 2017. PMID: 27104850
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery in the treatment of parasellar meningiomas: long-term volumetric evaluation.J Neurosurg. 2018 Feb;128(2):362-372. doi: 10.3171/2016.11.JNS161402. Epub 2017 Mar 24. J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 28338439
-
The Radiosurgery Society Case-Based Discussion of the Management of Head and Neck or Skull Base Paragangliomas with Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Radiotherapy.Pract Radiat Oncol. 2024 May-Jun;14(3):225-233. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2023.12.011. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38237891 Review.
Cited by
-
Neoplastic nerve lesions.Neurol Sci. 2022 May;43(5):3019-3038. doi: 10.1007/s10072-022-05951-x. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Neurol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35195810 Review.
-
Cognitive Decline Secondary to Therapeutic Brain Radiation-Similarities and Differences to Traumatic Brain Injury.Brain Sci. 2019 Apr 27;9(5):97. doi: 10.3390/brainsci9050097. Brain Sci. 2019. PMID: 31035608 Free PMC article.
-
Single- and Multi-Fraction Stereotactic Radiosurgery Dose Tolerances of the Optic Pathways.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 May 1;110(1):87-99. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.01.053. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 29534899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mannitol prior to radiosurgery reduces peritumoral edema and tumor volume of brain metastasis from lung primary.J Radiosurg SBRT. 2022;8(1):67-69. J Radiosurg SBRT. 2022. PMID: 35387410 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Target delineation and optimal radiosurgical dose for pituitary tumors.Radiat Oncol. 2016 Oct 11;11(1):135. doi: 10.1186/s13014-016-0710-y. Radiat Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27729088 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Patel SG, Singh B, Polluri A, Bridger PG, Cantu G, Cheesman AD, DeSa GM, Donald P, Fliss D, Gullane P, Janecka I, Kamata SE, Kowalski LP, Kraus DH, Levine PA, Dos Santos LR, Pradhan S, Schramm V, Snyderman C, Wei WI, Shah JP. Craniofacial surgery for malignant skull base tumors: report of an international collaborative study. Cancer. 2003;98:1179–1187. doi: 10.1002/cncr.11630. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vikram B, Chu FC. Radiation therapy for metastases to the base of the skull. Radiology. 1979;130:465–468. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

