Immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma with small double-stranded RNA
- PMID: 24886485
- PMCID: PMC4038722
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-338
Immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma with small double-stranded RNA
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignancies worldwide with limited therapeutic options. Since HCC has been shown to be immunogenic, immunotherapy is considered a promising therapeutic approach. Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), depending on their structure and sequence, can trigger the innate immune system, which can potentially enhance the adaptive anticancer immune response in the tumor-bearing subjects. Immunostimulatory properties of nucleic acids can be applied to develop adjuvants for HCC treatment.
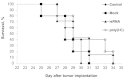
Methods: The transplantable HCC G-29 tumor in male CBA/LacSto (CBA) mice was used to study the effects of immunostimulatory RNA on tumor growth. Tumor size, metastases area in different organs of mice and mouse survival rate were analyzed. Furthermore the mouse serum IFN-α levels were measured using ELISA.
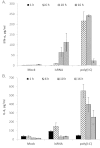
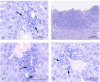
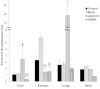
Results: In the present study, we found that a 19-bp RNA duplex (ImmunoStimulattory RNA or isRNA) with 3-nt overhangs at the 3'-ends of specific sequence displays immunostimulatory, antitumor, and antimetastatic activities in mice bearing HCC G-29. Our results demonstrate that isRNA strongly increases the level of interferon-α (IFN-α) by up to 25-fold relative to the level in mice injected with Lipofectamine alone (Mock), and to a lesser extent increases the level of proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) (by up to 5.5-fold relative to the Mock level), in mice blood serum. We showed that isRNA reliably (P < 0.05) inhibits primary tumor growth in mice compared to the mock group. Furthermore, injections of isRNA significantly enhanced necrotic processes in the center of the primary tumor, and decreased by twofold the width of the undifferentiated peripheral zone and the number of mitotic cells in this zone. The results showed that isRNA efficiently reduces the area of metastases in the liver, kidneys, and heart of CBA/LacSto mice with HCC.
Conclusions: The obtained results clearly demonstrate immunostimulatory and antimetastatic properties of the isRNAs in mice with HCC. Consequently, this short double-stranded RNA can be considered as a potential adjuvant for the therapy of HCC.
Figures


References
-
- Schütte K, Bornschein J, Malfertheiner P. Hepatocellular carcinoma–epidemiological trends and risk factors. Dig Dis. 2009;27:80–92. - PubMed
-
- Arii S, Yamaoka Y, Futagawa S, Inoue K, Kobayashi K, Kojiro M, Makuuchi M, Nakamura Y, Okita K, Yamada R. Results of surgical and nonsurgical treatment for small-sized hepatocellular carcinomas: a retrospective and nationwide survey in Japan. Hepatology. 2000;32:1224–1229. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2000.20456. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

