Phosphorylation of mTOR and S6RP predicts the efficacy of everolimus in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 24886512
- PMCID: PMC4041340
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-376
Phosphorylation of mTOR and S6RP predicts the efficacy of everolimus in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: The incidence of renal cell cancer (RCC) has been increasing for the past decade, and the 5-year survival for patients with metastatic RCC (mRCC) is rather low. Everolimus (RAD001), a new inhibitor for mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), is generally well tolerated, and demonstrates clinical benefit to patients with anti-VEGF-refractory mRCC. However, factors for selection of patients who may benefit from everolimus remain largely unknown. Here we aimed to explore potential molecular indicators for mRCC patients who may benefit from everolimus treatment.
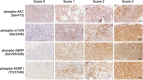
Methods: Paraffin-embedded tumor tissue specimens derived from 18 mRCC patients before everolimus treatment, who participated the phase 1b trial of everolimus in VEGF receptor (VEGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI)-refractory Chinese patients with mRCC (clinicaltrials.gov, NCT01152801), were examined for the expression levels of phosphorylated AKT, mTOR, eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) binding protein-1 (4EBP1) and 40S ribosomal protein S6 (S6RP) by immunohistochemistry. Clinical benefit rate (complete response [CR], partial response [PR], plus stable disease [SD] ≥ 6 months) and progression-free survival time (PFS) were correlated with expression levels of these mTOR-associated molecules.
Results: In these 18 patients, there were 1 PR, 15 SDs (including 9 SDs ≥ 6 months), and 2 progressive diseases (PD). The clinical benefit rate (CBR) was 55.6% (10/18), and the median PFS time was 8.4 months. Patients with positive expression of phospho-mTOR showed a better CBR (71.4% versus 0%, P = 0.023) and PFS time (11.3 versus 3.7 months, P = 0.001) than those patients with negative expression. The median PFS of patients with positive phospho-S6RP expression was longer (11.3 versus 3.7 months, P = 0.002) than that of patients negative for phospho-S6RP expression. However, expression levels of phospho-4EBP1 and phospho-AKT were unassociated to efficacy of everolimus treatment with respect to CBR and PFS. Co-expression of phosphorylated mTOR, S6RP and/or 4EBP1 may improve the predictive value of the biomarkers for patients treated with everolimus.
Conclusions: The expression levels of phospho-mTOR and phospho-S6RP may be potential predictive biomarkers for efficacy of everolimus in patients with mRCC. Combining examinations of phosphorylated mTOR, S6RP and/or 4EBP1 may be a potential strategy to select mRCC patients sensitive to mTOR inhibitor treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety and efficacy of everolimus in Chinese patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma resistant to vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy: an open-label phase 1b study.BMC Cancer. 2013 Mar 21;13:136. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-136. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23514360 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Expression level of phosphorylated-4E-binding protein 1 in radical nephrectomy specimens as a prognostic predictor in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors.Med Oncol. 2014 Jan;31(1):792. doi: 10.1007/s12032-013-0792-4. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Med Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24307346
-
First-line Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: an analysis of practice patterns from the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium.Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2014 Oct;12(5):335-40. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2014.03.003. Epub 2014 Mar 15. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24787966 Free PMC article.
-
Everolimus for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011 May;12(7):1143-55. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2011.571382. Epub 2011 Apr 7. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011. PMID: 21470068 Review.
-
Everolimus in renal cell carcinoma.Drugs Today (Barc). 2010 Aug;46(8):557-66. doi: 10.1358/dot.2010.46.8.1516824. Drugs Today (Barc). 2010. PMID: 20830316 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Effect of Repurposed Temsirolimus in Lung Adenocarcinoma Model.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Jul 24;9:778. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00778. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30087612 Free PMC article.
-
Metastatic role of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling activation by chemoradiotherapy in advanced rectal cancer.Cancer Sci. 2020 Apr;111(4):1291-1302. doi: 10.1111/cas.14332. Epub 2020 Feb 22. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 31997546 Free PMC article.
-
Methods to identify molecular expression of mTOR pathway: a rationale approach to stratify patients affected by clear cell renal cell carcinoma for more likely response to mTOR inhibitors.Am J Cancer Res. 2014 Nov 19;4(6):907-15. eCollection 2014. Am J Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25520878 Free PMC article.
-
The ribosomal protein S6 in renal cell carcinoma: functional relevance and potential as biomarker.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 5;7(1):418-32. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6225. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26506236 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Therapy Recommendations for Therapy Refractory Solid Tumors-Data from the Real-World Precision Medicine Platform MONDTI.J Pers Med. 2020 Oct 23;10(4):188. doi: 10.3390/jpm10040188. J Pers Med. 2020. PMID: 33114048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Oudard S, Hutson TE, Porta C, Bracarda S, Grünwald V, Thompson JA, Figlin RA, Hollaender N, Kay A, Ravaud A. Phase 3 trial of everolimus for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: final results and analysis of prognostic factors. Cancer. 2010;116:4256–4265. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25219. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yoshizawa A, Fukuoka J, Shimizu S, Shilo K, Franks TJ, Hewitt SM, Fujii T, Cordon-Cardo C, Jen J, Travis WD. Overexpression of phospho-eIF4E is associated with survival through AKT pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:240–248. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0986. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous