Synovial explant inflammatory mediator production corresponds to rheumatoid arthritis imaging hallmarks: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 24886513
- PMCID: PMC4078218
- DOI: 10.1186/ar4557
Synovial explant inflammatory mediator production corresponds to rheumatoid arthritis imaging hallmarks: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Introduction: Despite the widespread use of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and Doppler ultrasound for the detection of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) disease activity, little is known regarding the association of imaging-detected activity and synovial pathology. The purpose of this study was to compare site-specific release of inflammatory mediators and evaluate the corresponding anatomical sites by examining colour Doppler ultrasound (CDUS) and MRI scans.
Methods: RA patients were evaluated on the basis of CDUS and 3-T MRI scans and subsequently underwent synovectomy using a needle arthroscopic procedure of the hand joints. The synovial tissue specimens were incubated for 72 hours, and spontaneous release of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1), interleukin 6 (IL-6), macrophage inflammatory protein 1β (MIP-1β) and IL-8 was measured by performing multiplex immunoassays. Bone marrow oedema (BME), synovitis and erosion scores were estimated on the basis of the rheumatoid arthritis magnetic resonance imaging score (RAMRIS). Mixed models were used for the statistical analyses. Parsimony was achieved by omitting covariates with P > 0.1 from the statistical model.
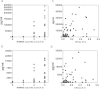
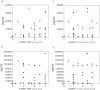
Results: Tissue samples from 58 synovial sites were obtained from 25 patients. MCP-1 was associated with CDUS activity (P = 0.009, approximate Spearman's ρ = 0.41), RAMRIS BME score (P = 0.01, approximate Spearman's ρ = 0.42) and RAMRIS erosion score (P = 0.03, approximate Spearman's ρ = 0.31). IL-6 was associated with RAMRIS synovitis score (P = 0.04, approximate Spearman's ρ = 0.50), BME score (P = 0.04, approximate Spearman's ρ = 0.31) and RAMRIS erosion score (P = 0.03, approximate Spearman's ρ = 0.35). MIP-1β was associated with CDUS activity (P = 0.02, approximate Spearman's ρ = 0.38) and RAMRIS synovitis scores (P = 0.02, approximate Spearman's ρ = 0.63). IL-8 associations with imaging outcome measures did not reach statistical significance.
Conclusions: The association between imaging activity and synovial inflammatory mediators underscores the high sensitivity of CDUS and MRI in the evaluation of RA disease activity. The associations found in our present study have different implications for synovial mediator releases and corresponding imaging signs. For example, MCP-1 and IL-6 were associated with both general inflammation and bone destruction, in contrast to MIP-1β, which was involved solely in general synovitis. The lack of association of IL-8 with synovitis was likely underestimated because of a large proportion of samples above assay detection limits among the patients with the highest synovitis scores.
Figures
References
-
- Schipper LG, Vermeer M, Kuper HH, Hoekstra MO, Haagsma CJ, Den Broeder AA, van Riel P, Fransen J, van de Laar MAFJ. A tight control treatment strategy aiming for remission in early rheumatoid arthritis is more effective than usual care treatment in daily clinical practice: a study of two cohorts in the Dutch Rheumatoid Arthritis Monitoring registry. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:845–850. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200274. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Landewé R, Breedveld FC, Dougados M, Emery P, Gaujoux-Viala C, Gorter S, Knevel R, Nam J, Schoels M, Aletaha D, Buch M, Gossec L, Huizinga T, Bijlsma JW, Burmester G, Combe B, Cutolo M, Gabay C, Gomez-Reino J, Kouloumas M, Kvien TK, Martin-Mola E, McInnes I, Pavelka K, van Riel P, Scholte M, Scott DL, Sokka T, Valesini G. et al.EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:964–975. doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.126532. A published erratum appears in Ann Rheum Dis 2011, 70:1519. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown AK, Quinn MA, Karim Z, Conaghan PG, Peterfy CG, Hensor E, Wakefield RJ, O'Connor PJ, Emery P. Presence of significant synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis patients with disease-modifying antirheumatic drug-induced clinical remission: evidence from an imaging study may explain structural progression. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:3761–3773. doi: 10.1002/art.22190. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brown AK, Conaghan PG, Karim Z, Quinn MA, Ikeda K, Peterfy CG, Hensor E, Wakefield RJ, O'Connor PJ, Emery P. An explanation for the apparent dissociation between clinical remission and continued structural deterioration in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:2958–2967. doi: 10.1002/art.23945. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO 3rd, Birnbaum NS, Burmester GR, Bykerk VP, Cohen MD, Combe B, Costenbader KH, Dougados M, Emery P, Ferraccioli G, Hazes JM, Hobbs K, Huizinga TW, Kavanaugh A, Kay J, Kvien TK, Laing T, Mease P, Ménard HA, Moreland LW, Naden RL, Pincus T, Smolen JS, Stanislawska-Biernat E, Symmons D. et al.Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2569–2581. doi: 10.1002/art.27584. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

