Use of antagonists and morpholinos in loss-of-function analyses: estrogen receptor ESR2a mediates the effects of 17alpha-ethinylestradiol on primordial germ cell distribution in zebrafish
- PMID: 24886565
- PMCID: PMC4038371
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7827-12-40
Use of antagonists and morpholinos in loss-of-function analyses: estrogen receptor ESR2a mediates the effects of 17alpha-ethinylestradiol on primordial germ cell distribution in zebrafish
Abstract
Background: Various chemicals released into the aquatic environment adversely affect the reproductive system of fish, particularly by changing gonad structure and function. 17alpha-ethinylestradiol (EE2) is a potent environmental estrogen that disrupts sexual differentiation and normal reproduction in fish. Previous studies have shown that exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) disrupts the migration of primordial germ cells (PGCs) in zebrafish.
Methods: To investigate the effects of EE2 exposure on PGC migration, zebrafish embryos were injected with gfp-nanos mRNA to label PGCs and subsequently exposed to different concentrations of EE2. Typical estrogen receptor antagonist treatment and morpholino knockdown experiments were used to identify functional estrogen receptors that mediate the effects of EE2.
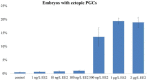
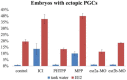
Results: The migration of PGCs was disrupted after exposure to high concentrations of EE2 (1 mirog/L). Loss-of-function analyses were performed for estrogen receptor ESR1, ESR2a, and ESR2b, and only loss of ESR2a resulted in a decreased number of ectopic PGCs following exposure to 1 mirog/L EE2.
Conclusions: EE2 exposure disrupts PGC migration and distribution, and this effect is mediated through the estrogen receptor ESR2a.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Paternal exposure to environmental 17-alpha-ethinylestradiol concentrations modifies testicular transcription, affecting the sperm transcript content and the offspring performance in zebrafish.Aquat Toxicol. 2017 Dec;193:18-29. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.09.025. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Aquat Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 29028550
-
Development and recovery of histopathological alterations in the gonads of zebrafish (Danio rerio) after single and combined exposure to endocrine disruptors (17α-ethinylestradiol and fadrozole).Aquat Toxicol. 2016 Jun;175:90-105. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.03.014. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Aquat Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27002526
-
Effects of antiandrogenic progestins, chlormadinone and cyproterone acetate, and the estrogen 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2), and their mixtures: Transactivation with human and rainbowfish hormone receptors and transcriptional effects in zebrafish (Danio rerio) eleuthero-embryos.Aquat Toxicol. 2017 Jan;182:142-162. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.11.001. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Aquat Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27907851
-
Estrogens as immunotoxicants: 17α-ethinylestradiol exposure retards thymus development in zebrafish (Danio rerio).Aquat Toxicol. 2022 Jan;242:106025. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2021.106025. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Aquat Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 34837781
-
Twenty years of transcriptomics, 17alpha-ethinylestradiol, and fish.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2020 Jan 15;286:113325. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2019.113325. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 31733209 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the estrogen receptor alpha as a possible target of bifenthrin effects in the estrogenic and dopaminergic signaling pathways in zebrafish embryos.Sci Total Environ. 2019 Feb 15;651(Pt 2):2424-2431. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.079. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Sci Total Environ. 2019. PMID: 30336432 Free PMC article.
-
Embryonic Exposure to Bisphenol A Impairs Primordial Germ Cell Migration without Jeopardizing Male Breeding Capacity.Biomolecules. 2019 Jul 25;9(8):307. doi: 10.3390/biom9080307. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31349731 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR Fish Reel in Novel Roles for Estrogen Receptors in Reproduction.Endocrinology. 2017 Jul 1;158(7):2082-2083. doi: 10.1210/en.2017-00417. Endocrinology. 2017. PMID: 28881866 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Estrogen Receptor β2 Oversees Germ Cell Maintenance and Gonadal Sex Differentiation in Medaka, Oryzias latipes.Stem Cell Reports. 2019 Aug 13;13(2):419-433. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2019.07.013. Stem Cell Reports. 2019. PMID: 31412286 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

