Sick leave patterns in common musculoskeletal disorders--a study of doctor prescribed sick leave
- PMID: 24886568
- PMCID: PMC4060756
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-15-176
Sick leave patterns in common musculoskeletal disorders--a study of doctor prescribed sick leave
Abstract
Background: Comparative data on sick leave within musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) is limited. Our objective was to give a descriptive overview of sick leave patterns in different MSDs.
Methods: Using electronic medical records, we collected information on dates and diagnostic codes for all available sick leave certificates, during 2 years (2009-2010), in the North Western part of the Skåne region in Sweden (22 public primary health care centres and two general hospitals). Using the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 10 codes on the certificates we studied duration, age and sex distribution and recurrent periods of sick leave for six strategically chosen MSDs; low back pain (M54) disc disorders (M51), knee osteoarthritis (M17) hip osteoarthritis (M16) rheumatoid arthritis (M05-M06) and myalgia (M79).
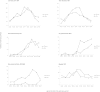
Results: All together 20 251 sick leave periods were issued for 16 673 individuals 16-64 years of age (53% women). Out of the selected disorders, low back pain and myalgia had the shortest sick leave periods, with a mean of 26 and 27 days, respectively, while disc disorders and rheumatoid arthritis had the longest periods with a mean of 150 and 147 days. For low back pain and myalgia 27% and 26% of all sick leave was short (8-14 days) and only 11% and 13%, were long (≥90 days). For the other selected MSDs, less than 5% of the periods were short. For disc disorders, hip osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, more than 60% of the periods were long (p > 0.001). For back disorders and myalgia most periods were issued in the age groups between 40-49, with similar patterns for women and men. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis had most periods in the age groups of 50-64, and patterns for women and men differed. Low back pain, rheumatoid arthritis and myalgia had the greatest share of recurrent sick leave (31%, 34% and 32% respectively).
Conclusion: Duration, age and sex distribution and numbers of recurrent sick leave varies considerably between different MSDs. This underscores the importance of using specified diagnosis, in sick leave research as well as in planning of treatment and rehabilitation and evaluation of prognosis.
Figures
References
-
- Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, Shibuya K, Salomon JA, Abdalla S, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Ackerman I, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, Ali MK, Alvarado M, Anderson HR, Anderson LM, Andrews KG, Atkinson C, Baddour LM, Bahalim AN, Barker-Collo S, Barrero LH, Bartels DH, Basanez MG, Baxter A, Bell ML, Benjamin EJ, Bennett D. et al.Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2163–2196. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Urwin M, Symmons D, Allison T, Brammah T, Busby H, Roxby M, Simmons A, Williams G. Estimating the burden of musculoskeletal disorders in the community: the comparative prevalence of symptoms at different anatomical sites, and the relation to social deprivation. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998;57(11):649–655. doi: 10.1136/ard.57.11.649. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources