Lentiviral and targeted cellular barcoding reveals ongoing clonal dynamics of cell lines in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 24886633
- PMCID: PMC4073073
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-5-r75
Lentiviral and targeted cellular barcoding reveals ongoing clonal dynamics of cell lines in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
Background: Cell lines are often regarded as clonal, even though this simplifies what is known about mutagenesis, transformation and other processes that destabilize them over time. Monitoring these clonal dynamics is important for multiple areas of biomedical research, including stem cell and cancer biology. Tracking the contributions of individual cells to large populations, however, has been constrained by limitations in sensitivity and complexity.
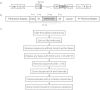
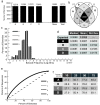
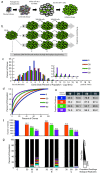
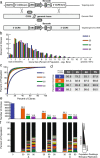
Results: We utilize cellular barcoding methods to simultaneously track the clonal contributions of tens of thousands of cells. We demonstrate that even with optimal culturing conditions, common cell lines including HeLa, K562 and HEK-293 T exhibit ongoing clonal dynamics. Starting a population with a single clone diminishes but does not eradicate this phenomenon. Next, we compare lentiviral and zinc-finger nuclease barcode insertion approaches, finding that the zinc-finger nuclease protocol surprisingly results in reduced clonal diversity. We also document the expected reduction in clonal complexity when cells are challenged with genotoxic stress. Finally, we demonstrate that xenografts maintain clonal diversity to a greater extent than in vitro culturing of the human non-small-cell lung cancer cell line HCC827.
Conclusions: We demonstrate the feasibility of tracking and quantifying the clonal dynamics of entire cell populations within multiple cultured cell lines. Our results suggest that cell heterogeneity should be considered in the design and interpretation of in vitro culture experiments. Aside from clonal cell lines, we propose that cellular barcoding could prove valuable in modeling the clonal behavior of heterogeneous cell populations over time, including tumor populations treated with chemotherapeutic agents.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clonal tracking using embedded viral barcoding and high-throughput sequencing.Nat Protoc. 2020 Apr;15(4):1436-1458. doi: 10.1038/s41596-019-0290-z. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Nat Protoc. 2020. PMID: 32132718 Free PMC article.
-
Massive Clonal Selection and Transiently Contributing Clones During Expansion of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Cultures Revealed by Lentiviral RGB-Barcode Technology.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016 May;5(5):591-601. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0176. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27034413 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneity of young and aged murine hematopoietic stem cells revealed by quantitative clonal analysis using cellular barcoding.Blood. 2013 Jul 25;122(4):523-32. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-01-481135. Epub 2013 May 29. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23719303
-
Cellular barcoding to decipher clonal dynamics in disease.Science. 2022 Oct 14;378(6616):eabm5874. doi: 10.1126/science.abm5874. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Science. 2022. PMID: 36227997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluorescent genetic barcoding for cellular multiplex analyses.Exp Hematol. 2018 Nov;67:10-17. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2018.08.001. Epub 2018 Aug 8. Exp Hematol. 2018. PMID: 30098396 Review.
Cited by
-
Computational Stem Cell Biology: Open Questions and Guiding Principles.Cell Stem Cell. 2021 Jan 7;28(1):20-32. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2020.12.012. Cell Stem Cell. 2021. PMID: 33417869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in prospective single-cell lineage barcoding and their applications in research.Genome Res. 2024 Dec 23;34(12):2147-2162. doi: 10.1101/gr.278944.124. Genome Res. 2024. PMID: 39572229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Limitations and optimizations of cellular lineages tracking.PLoS Comput Biol. 2025 Apr 14;21(4):e1012880. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012880. eCollection 2025 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2025. PMID: 40228207 Free PMC article.
-
Reproducibility of Illumina platform deep sequencing errors allows accurate determination of DNA barcodes in cells.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Apr 2;17:151. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-0999-4. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27038897 Free PMC article.
-
Clonal barcoding with qPCR detection enables live cell functional analyses for cancer research.Nat Commun. 2022 Jul 4;13(1):3837. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31536-5. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35788590 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

