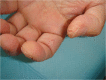
Mechanic's hands revisited: is this sign still useful for diagnosis in patients with lung involvement of collagen vascular diseases?
- PMID: 24886713
- PMCID: PMC4035896
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-303
Mechanic's hands revisited: is this sign still useful for diagnosis in patients with lung involvement of collagen vascular diseases?
Abstract
Background: The presence of "mechanic's hands" is one of the clinical clues for collagen vascular diseases. However, the exact relevance of "mechanic's hands" in collagen vascular diseases has not been well documented. The aim of this study was to clarify the relevance of "mechanic's hands" to collagen vascular diseases including various skin lesions and interstitial pneumonia.
Methods: A retrospective review of the medical records of patients with "mechanic's hands" at our hospital between April 2011 and December 2012 was conducted. A PubMed search was also conducted using the term "mechanic's hands".
Results: Four patients in our institution and 40 patients obtained from PubMed who had "mechanic's hands" were identified. The most frequent diseases were DM/amyopathic DM (n = 24, 54.5%) and anti-ARS syndrome (n = 17, 38.6%). In these patients, the major skin lesions associated with "mechanic's hands" were periungual erythema (n = 23, 52.3%), Gottron's sign (n = 17, 38.6%), heliotrope rash (n = 10, 22.7%), Raynaud's phenomenon (n = 9, 20.5%), and anti-ARS syndrome (n = 17, 38.6%). Six cases (2 DM, 4 anti-ARS syndrome) had only "mechanic's hands". Antibodies to anti-ARS (n = 24) were Jo-1 (n = 19), PL-7 (n = 3), OJ (n = 1), and PL-12 (n = 1).
Conclusion: The presence of "mechanic's hands" together with diverse skin lesions could be a clinical clue to the diagnosis of lung involvement associated with collagen vascular diseases, especially in anti-ARS syndrome or DM/amyopathic DM.
Figures
References
-
- Tanimoto K, Nakano K, Kano S, Mori S, Ueki H, Nishitani H, Sato T, Kiuchi T, Ohashi Y. Classification criteria for polymyositis and dermatomyositis. J Rheumatol Apr. 1995;22(4):668–674. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous