Differential regulation of Gli proteins by Sufu in the lung affects PDGF signaling and myofibroblast development
- PMID: 24886827
- PMCID: PMC4106470
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.05.014
Differential regulation of Gli proteins by Sufu in the lung affects PDGF signaling and myofibroblast development
Abstract
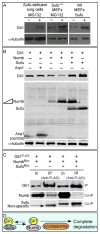
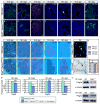
Mammalian Hedgehog (Hh) signaling relies on three Gli transcription factors to mediate Hh responses. This process is controlled in part by a major negative regulator, Sufu, through its effects on Gli protein level, distribution and activity. In this report, we showed that Sufu regulates Gli1 protein levels by antagonizing Numb/Itch. Otherwise, Numb/Itch would induce Gli1 protein degradation. This is in contrast to inhibition of Spop-mediated degradation of Gli2/3 by Sufu. Thus, controlling protein levels of all three Gli genes by Sufu is a conserved mechanism to modulate Hh responses albeit via distinct pathways. These findings in cell-based assays were further validated in vivo. In analyzing how Sufu controls Gli proteins in different tissues, we discovered that loss of Sufu in the lung exerts different effects on Hh target genes. Hh targets Ptch1/Hhip are upregulated in Sufu-deficient lungs, consistent with Hh pathway activation. Surprisingly, protein levels of Hh target Gli1 are reduced. We also found that myofibroblasts are absent from many prospective alveoli of Sufu-deficient lungs. Myofibroblast development is dependent on PDGF signaling. Interestingly, analysis of the Pdgfra promoter revealed a canonical Gli-binding site where Gli1 resides. These studies support a model in which loss of Sufu contributes to compromised Pdgfra activation and disrupts myofibroblast development in the lung. Our work illustrates the unappreciated complexity of Hh responses where distinct Hh targets could respond differently depending on the availability of Gli proteins that control their expression.
Keywords: Gli; Hedgehog; Lung; Myofibroblast; PDGF; Sufu.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cilium-independent regulation of Gli protein function by Sufu in Hedgehog signaling is evolutionarily conserved.Genes Dev. 2009 Aug 15;23(16):1910-28. doi: 10.1101/gad.1794109. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19684112 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Sufu activity by p66β and Mycbp provides new insight into vertebrate Hedgehog signaling.Genes Dev. 2014 Nov 15;28(22):2547-63. doi: 10.1101/gad.249425.114. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 25403183 Free PMC article.
-
Nek2A/SuFu feedback loop regulates Gli-mediated Hedgehog signaling pathway.Int J Oncol. 2017 Feb;50(2):373-380. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3819. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28035348 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog Signaling and Truncated GLI1 in Cancer.Cells. 2020 Sep 17;9(9):2114. doi: 10.3390/cells9092114. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32957513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Primers on molecular pathways GLI: more than just Hedgehog?Pancreatology. 2008;8(3):227-9. doi: 10.1159/000134271. Epub 2008 May 22. Pancreatology. 2008. PMID: 18497536 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential requirement of SUFU in tissue development discovered in a hypomorphic mouse model.Dev Biol. 2017 Sep 1;429(1):132-146. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.06.037. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28688895 Free PMC article.
-
MEKK2 and MEKK3 suppress Hedgehog pathway-dependent medulloblastoma by inhibiting GLI1 function.Oncogene. 2018 Jul;37(28):3864-3878. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0249-5. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29662197 Free PMC article.
-
Sonic hedgehog signaling in the lung. From development to disease.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015 Jan;52(1):1-13. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2014-0132TR. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25068457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of Suppressor of Fused in Mid-Corticogenesis Leads to the Expansion of Intermediate Progenitors.J Dev Biol. 2016 Dec;4(4):29. doi: 10.3390/jdb4040029. Epub 2016 Sep 29. J Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 28781964 Free PMC article.
-
Suppressor of Fused Inhibits Skin Wound Healing.Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2020 May 1;9(5):233-244. doi: 10.1089/wound.2018.0890. Epub 2020 Mar 19. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2020. PMID: 32226648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology (Wiley) 2003
-
- Bai CB, Auerbach W, Lee JS, Stephen D, Joyner AL. Gli2, but not Gli1, is required for initial Shh signaling and ectopic activation of the Shh pathway. Development. 2002;129:4753–4761. - PubMed
-
- Bai CB, Stephen D, Joyner AL. All mouse ventral spinal cord patterning by hedgehog is Gli dependent and involves an activator function of Gli3. Dev Cell. 2004;6:103–115. - PubMed
-
- Barnfield PC, Zhang X, Thanabalasingham V, Yoshida M, Hui CC. Negative regulation of Gli1 and Gli2 activator function by Suppressor of fused through multiple mechanisms. Differentiation; research in biological diversity. 2005;73:397–405. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

