Prostaglandin E2 excitatory effects on guinea pig urinary bladder smooth muscle: a novel regulatory mechanism mediated by large-conductance voltage- and Ca2+-activated K+ channels
- PMID: 24886877
- PMCID: PMC4107080
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.05.042
Prostaglandin E2 excitatory effects on guinea pig urinary bladder smooth muscle: a novel regulatory mechanism mediated by large-conductance voltage- and Ca2+-activated K+ channels
Abstract
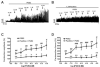
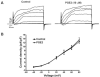
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) is an essential signaling molecule involved in the regulation of detrusor smooth muscle (DSM) function. However, the underlying regulatory mechanism by which PGE2 augments DSM cell excitability and contractility is not well understood. Here, we investigated whether PGE2 inhibits the large conductance voltage- and Ca(2+)-activated K(+) (BK) channels in guinea pig DSM, thereby increasing DSM excitability and contractility. We used a multidisciplinary experimental approach including amphotericin-B perforated patch-clamp electrophysiology and live-cell Ca(2+) imaging in native freshly-isolated DSM cells, isometric tension recordings of intact DSM strips, and pharmacological tools to investigate BK channel regulation by PGE2 in guinea pig DSM. PGE2 increased the spontaneous phasic contractions of isolated DSM strips in a concentration-dependent manner (10 nM-10 µM). BK channel inhibition with paxilline (1 µM) attenuated the PGE2-induced DSM phasic contractions, suggesting that BK channels are involved in the mechanism of PGE2-induced DSM contractions. PGE2 (10 µM) increased the intracellular Ca(2+) levels in freshly-isolated DSM cells. PGE2 (10 µM) also caused an inhibition of the amplitude and frequency of spontaneous transient BK currents in DSM cells. Moreover, PGE2 (10 µM) did not affect the amplitude of whole cell steady-state BK currents in DSM cells. Our findings provide strong experimental evidence that PGE2 leads to an inhibition of the spontaneous transient BK currents, elevation of intracellular Ca(2+) levels in freshly-isolated DSM cells, and augmentation of DSM phasic contractions. Thus, we have revealed a novel mechanism that BK channels mediate PGE2-induced contractions in guinea pig DSM.
Keywords: Ca(2+) imaging; Detrusor; Patch-clamp; Prostaglandin E(2).
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Large-conductance voltage- and Ca2+-activated K+ channel regulation by protein kinase C in guinea pig urinary bladder smooth muscle.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014 Mar 1;306(5):C460-70. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00325.2013. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24352333 Free PMC article.
-
Novel mechanism of hydrogen sulfide-induced guinea pig urinary bladder smooth muscle contraction: role of BK channels and cholinergic neurotransmission.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015 Jul 15;309(2):C107-16. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00021.2015. Epub 2015 May 6. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25948731 Free PMC article.
-
BK channel-mediated relaxation of urinary bladder smooth muscle: a novel paradigm for phosphodiesterase type 4 regulation of bladder function.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014 Apr;349(1):56-65. doi: 10.1124/jpet.113.210708. Epub 2014 Jan 23. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014. PMID: 24459245 Free PMC article.
-
Central role of the BK channel in urinary bladder smooth muscle physiology and pathophysiology.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014 Sep 15;307(6):R571-84. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00142.2014. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24990859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urinary bladder smooth muscle ion channels: expression, function, and regulation in health and disease.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020 Aug 1;319(2):F257-F283. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00048.2020. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32628539 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prostaglandin E2 excitatory effects on rat urinary bladder: a comparison between the β-adrenoceptor modulation of non-voiding activity in vivo and micro-contractile activity in vitro.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015 Jul;388(7):727-35. doi: 10.1007/s00210-015-1139-9. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26063630
-
TRP Channel Agonists Activate Different Afferent Neuromodulatory Mechanisms in Guinea Pig Urinary Bladder.Front Physiol. 2021 Jun 24;12:692719. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.692719. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34248678 Free PMC article.
-
BK channel activators and their therapeutic perspectives.Front Physiol. 2014 Oct 9;5:389. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00389. eCollection 2014. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25346695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The omega-3 fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid is required for normal alcohol response behaviors in C. elegans.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 27;9(8):e105999. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105999. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25162400 Free PMC article.
-
PGE2 receptors in detrusor muscle: Drugging the undruggable for urgency.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Feb;184:114363. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114363. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33309520 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson KE. Pharmacology of lower urinary tract smooth muscles and penile erectile tissues. Pharmacol Rev. 1993;45:253–308. - PubMed
-
- Aoki K, Hirayama A, Tanaka N, Yoneda T, Yoshida K, Fujimoto K, Hirao Y. A higher level of prostaglandin E2 in the urinary bladder in young boys and boys with lower urinary tract obstruction. Biomed Res. 2009;30:343–347. - PubMed
-
- Bos CL, Richel DJ, Ritsema T, Peppelenbosch MP, Versteeg HH. Prostanoids and prostanoid receptors in signal transduction. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;36:1187–1205. - PubMed
-
- Brown WW, Zenser TV, Davis BB. Prostaglandin E2 production by rabbit urinary bladder. Am J Physiol. 1980;239:F452–458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

