A meta analysis of lumbar spinal fusion surgery using bone morphogenetic proteins and autologous iliac crest bone graft
- PMID: 24886911
- PMCID: PMC4041715
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097049
A meta analysis of lumbar spinal fusion surgery using bone morphogenetic proteins and autologous iliac crest bone graft
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e116460
Abstract
Background: Bone morphogenetic protein (BMPs) as a substitute for iliac crest bone graft (ICBG) has been increasingly widely used in lumbar fusion. The purpose of this study is to systematically compare the effectiveness and safety of fusion with BMPs for the treatment of lumbar disease.
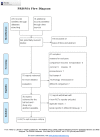
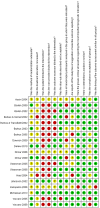
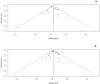
Methods: Cochrane review methods were used to analyze all relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published up to nov 2013.
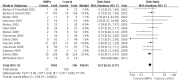
Results: 19 RCTs (1,852 patients) met the inclusion criteria. BMPs group significantly increased fusion rate (RR: 1.13; 95% CI 1.05-1.23, P = 0.001), while there was no statistical difference in overall success of clinical outcomes (RR: 1.04; 95% CI 0.95-1.13, P = 0.38) and complications (RR: 0.96; 95% CI 0.85-1.09, p = 0.54). A significant reduction of the reoperation rate was found in BMPs group (RR: 0.57; 95% CI 0.42-0.77, p = 0.0002). Significant difference was found in the operating time (MD-0.32; 95% CI-0.55, -0.08; P = 0.009), but no significant difference was found in the blood loss, the hospital stay, patient satisfaction, and work status.
Conclusion: Compared with ICBG, BMPs in lumbar fusion can increase the fusion rate, while reduce the reoperation rate and operating time. However, it doesn't increase the complication rate, the amount of blood loss and hospital stay. No significant difference was found in the overall success of clinical outcome of the two groups.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


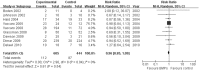

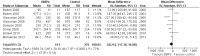

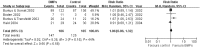


Similar articles
-
Comparative Clinical Effectiveness and Safety of Bone Morphogenetic Protein Versus Autologous Iliac Crest Bone Graft in Lumbar Fusion: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020 Jun 15;45(12):E729-E741. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000003372. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020. PMID: 31923133 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the use of rhBMP-7 versus iliac crest autograft in single-level lumbar fusion: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Bone Miner Metab. 2018 Jan;36(1):119-127. doi: 10.1007/s00774-017-0821-z. Epub 2017 Mar 24. J Bone Miner Metab. 2018. PMID: 28342094
-
Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 versus autogenous iliac crest bone graft for lumbar fusion: a meta-analysis of ten randomized controlled trials.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012 Dec;132(12):1725-40. doi: 10.1007/s00402-012-1607-3. Epub 2012 Sep 1. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012. PMID: 22941273
-
Perioperative complications of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 on an absorbable collagen sponge versus iliac crest bone graft for posterior cervical arthrodesis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009 Jun 1;34(13):1390-4. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181a2da08. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009. PMID: 19440166
-
Efficacy of autologous iliac crest bone graft and bone morphogenetic proteins for posterolateral fusion of lumbar spine: a meta-analysis of the results.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008 Sep 1;33(19):E680-92. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181844eca. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008. PMID: 18758349
Cited by
-
Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Use in Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery: Comparative Analysis and Healthcare Utilization at 24 Months' Follow-up.Global Spine J. 2022 Jan;12(1):92-101. doi: 10.1177/2192568220947377. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Global Spine J. 2022. PMID: 32844671 Free PMC article.
-
Vascularized Posterior Iliac Crest Bone Grafting: Indications, Techniques, Clinical Outcomes, and Alternatives.Semin Plast Surg. 2021 Feb;35(1):37-40. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1725986. Epub 2021 May 10. Semin Plast Surg. 2021. PMID: 33994877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computationally designed lattices with tuned properties for tissue engineering using 3D printing.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 10;12(8):e0182902. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182902. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28797066 Free PMC article.
-
Complication Rates in Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF) Surgery With Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2: Medicare Population.Global Spine J. 2017 Dec;7(8):770-773. doi: 10.1177/2192568217696695. Epub 2017 May 16. Global Spine J. 2017. PMID: 29238641 Free PMC article.
-
Interbody options in lumbar fusion.J Spine Surg. 2019 Jun;5(Suppl 1):S19-S24. doi: 10.21037/jss.2019.04.04. J Spine Surg. 2019. PMID: 31380489 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arrington ED, Smith WJ, Chambers HG, Bucknell AL, Davino NA (1996) Complications of iliac crest bone graft harvesting. Clin Orthop Relat Res 329: 300–309 doi:10.1097/00003086-199608000-00037 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Urist MR (1965) Bone Formation by autoinduction. Science 150: 893–899 doi:10.1126/science. 150.3698.893 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Celeste AJ, Iannazzi JA, Taylor RC, Hewick RM, Rosen V, et al. (1990) Identification of transforming growth factor beta family members present in bone-inductive protein purified from bovine bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 9843–9847 doi:10.1073/pnas.87.24.9843 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33: 159–174 doi:10.2307/2529310 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Viera AJ, Garrett JM (2005) Understanding interobserver agreement: the kappa statistic.Fam Med. 37: 360–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

