Global metabolite profiling of synovial fluid for the specific diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis from other inflammatory arthritis
- PMID: 24887281
- PMCID: PMC4041724
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097501
Global metabolite profiling of synovial fluid for the specific diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis from other inflammatory arthritis
Abstract
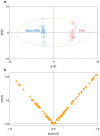
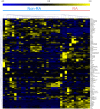
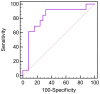
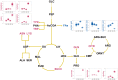
Currently, reliable biomarkers that can be used to distinguish rheumatoid arthritis (RA) from other inflammatory diseases are unavailable. To find possible distinctive metabolic patterns and biomarker candidates for RA, we performed global metabolite profiling of synovial fluid samples. Synovial fluid samples from 38 patients with RA, ankylosing spondylitis, Behçet's disease, and gout were analyzed by gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC/TOF MS). Orthogonal partial least-squares discriminant and hierarchical clustering analyses were performed for the discrimination of RA and non-RA groups. Variable importance for projection values were determined, and the Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test and the breakdown and one-way analysis of variance were conducted to identify potential biomarkers for RA. A total of 105 metabolites were identified from synovial fluid samples. The score plot of orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis showed significant discrimination between the RA and non-RA groups. The 20 metabolites, including citrulline, succinate, glutamine, octadecanol, isopalmitic acid, and glycerol, were identified as potential biomarkers for RA. These metabolites were found to be associated with the urea and TCA cycles as well as fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. The metabolomic analysis results demonstrated that global metabolite profiling by GC/TOF MS might be a useful tool for the effective diagnosis and further understanding of RA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Cammarata RJ, Rodnan GP, Fennell RH (1967) Serum anti-γ-globulin and antinuclear factors in the aged. JAMA-J Am Med Assoc 199: 455–458. - PubMed
-
- Litwin SD, Singer JM (1965) Studies of the incidence and significance of anti-gamma globulin factors in the aging. Arthritis Rheum 8: 538–550. - PubMed
-
- Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, de Jong BAW, Berglin E, Hallmans G, Wadell G, et al. (2003) Antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptide and IgA rheumatoid factor predict the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 48: 2741–2749. - PubMed
-
- Humphreys JH, Symmons DP (2012) Postpublication validation of the 2010 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: where do we stand? Curr Opin Rheumatol 25(2): 157–163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

