The mechanistic target for rapamycin pathway is related to the phosphorylation score for estrogen receptor-α in human breast tumors in vivo
- PMID: 24887419
- PMCID: PMC4076628
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr3660
The mechanistic target for rapamycin pathway is related to the phosphorylation score for estrogen receptor-α in human breast tumors in vivo
Abstract
Introduction: A phosphorylation score for estrogen receptor-alpha (ERα), called P7 score, was shown previously to be an independent prognostic factor in breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen. Since mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) activation is implicated in resistance to endocrine therapy in breast cancer we determined whether mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) activation, measured by phosphorylation on S2448 (p-mTOR), was associated with the P7-score and/or clinical outcome in the same cohort.
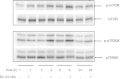
Methods: mTOR phosphorylation status was determined at S2448 residue in vivo by immunohistochemistry in a cohort of more than 400 well-characterized ERα positive breast tumors. MCF7 cells were treated with estrogen and activation of mTOR pathway was determined by Western blotting.
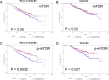
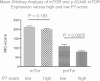
Results: Contrary to earlier reports, p-mTOR expression, measured by immunohistochemistry, was negatively associated with size and nodal status. Additionally, p-S2448 mTOR expression was positively correlated with p-S118- ERα, p-S167-ERα and p-S282-ERα but negatively correlated with p-T311- ERα. Consistent with these, p-S2448 mTOR was negatively associated with P7-score and was significantly associated with overall survival (OS) (hazard ratio (HR) = 0.61, P = 0.028, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.39 to 0.95, n = 337) and relapse-free survival (HR = 0.58, P = 0.0032, 95% CI 0.41 to 0.83, n = 337) following univariate but not multivariate analysis. Furthermore, we show that estrogen can regulate phosphorylation of mTOR and its down stream target p70S6 kinase. Additionally, recombinant mTOR can phosphorylate ERα in vitro.
Conclusions: These data suggest that in breast tumors where there is intact estrogen regulated signaling, mTOR is regulated by estrogen and therefore associated with an increased likelihood of responsiveness to endocrine therapy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
microRNA regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin expression and activity controls estrogen receptor function and RAD001 sensitivity.Mol Cancer. 2014 Oct 6;13:229. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-229. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25283550 Free PMC article.
-
mTORC1 directly phosphorylates and activates ERα upon estrogen stimulation.Oncogene. 2016 Jul 7;35(27):3535-43. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.414. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26522726 Free PMC article.
-
Serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 (SGK1) activation in breast cancer: requirement for mTORC1 activity associates with ER-alpha expression.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Sep;135(2):469-79. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-2161-y. Epub 2012 Jul 29. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 22842983 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of estrogen receptor phosphorylation.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2011 Jan 19;18(1):R1-14. doi: 10.1677/ERC-10-0070. Print 2011 Feb. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21149515 Review.
-
Crosstalk of methylation and tamoxifen in breast cancer (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2024 Oct;30(4):180. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13304. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 39129315 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphoproteome Analysis Reveals Estrogen-ER Pathway as a Modulator of mTOR Activity Via DEPTOR.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019 Aug;18(8):1607-1618. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA119.001506. Epub 2019 Jun 12. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 31189691 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear TIGAR mediates an epigenetic and metabolic autoregulatory loop via NRF2 in cancer therapeutic resistance.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Apr;12(4):1871-1884. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.10.015. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35847493 Free PMC article.
-
The variable association between expression and methylation of estrogen receptors and the survival of patients with different tumors.Clin Transl Med. 2020 Jun;10(2):e49. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.49. Epub 2020 Jun 14. Clin Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32536040 Free PMC article.
-
FOXK2 transcription factor suppresses ERα-positive breast cancer cell growth through down-regulating the stability of ERα via mechanism involving BRCA1/BARD1.Sci Rep. 2015 Mar 5;5:8796. doi: 10.1038/srep08796. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25740706 Free PMC article.
-
Body fatness and mTOR pathway activation of breast cancer in the Women's Circle of Health Study.NPJ Breast Cancer. 2020 Sep 21;6:45. doi: 10.1038/s41523-020-00187-4. eCollection 2020. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33024820 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali S, Coombes R. Endocrine-responsive breast cancer and strategies for combating resistance. Nature Rev. 2002;2:101–112. - PubMed
-
- Skliris GP, Rowan BG, Al-Dhaheri M, Williams C, Troup S, Begic S, Parisien M, Watson PH, Murphy LC. Immunohistochemical validation of multiple phospho-specific epitopes for estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) in tissue microarrays of ERalpha positive human breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009;118:443–453. doi: 10.1007/s10549-008-0267-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

