Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink
- PMID: 24887553
- PMCID: PMC4059935
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4935
Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink
Abstract
The ability to print and pattern all the components that make up a tissue (cells and matrix materials) in three dimensions to generate structures similar to tissues is an exciting prospect of bioprinting. However, the majority of the matrix materials used so far for bioprinting cannot represent the complexity of natural extracellular matrix (ECM) and thus are unable to reconstitute the intrinsic cellular morphologies and functions. Here, we develop a method for the bioprinting of cell-laden constructs with novel decellularized extracellular matrix (dECM) bioink capable of providing an optimized microenvironment conducive to the growth of three-dimensional structured tissue. We show the versatility and flexibility of the developed bioprinting process using tissue-specific dECM bioinks, including adipose, cartilage and heart tissues, capable of providing crucial cues for cells engraftment, survival and long-term function. We achieve high cell viability and functionality of the printed dECM structures using our bioprinting method.
Figures
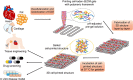

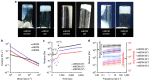
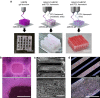
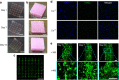
Comment in
-
Technology: The promise of printing.Nature. 2016 Dec 7;540(7632):S56-S57. doi: 10.1038/540S56a. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27926696 No abstract available.
References
-
- Griffith L. G. & Naughton G. Tissue engineering—current challenges and expanding opportunities. Science 295, 1009–1014 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Gaetani R. et al. Cardiac tissue engineering using tissue printing technology and human cardiac progenitor cells. Biomaterials 33, 1782–1790 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Falconnet D., Csucs G., Michelle Grandin H. & Textor M. Surface engineering approaches to micropattern surfaces for cell-based assays. Biomaterials 27, 3044–3063 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Chang R., Nam J. & Sun W. Direct cell writing of 3D microorgan for in vitro pharmacokinetic model. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 14, 157–166 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Fischbach C. et al. Engineering tumors with 3D scaffolds. Nat. Methods 4, 855–860 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

